尼可地尔治疗高龄冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者的疗效观察
作者: 马章鲁
【摘要】 目的 探讨尼可地尔对高龄冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者疗效及对患者血管内皮功能和心功能影响。方法 选择医院于2019年9月- 2021年9月收治的冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者142例作为研究对象,依据组间性别、年龄、纽约心脏病协会(NYHA)心功能分级、基础疾病分为观察组71例与对照组71例。对照组患者采用常规治疗,观察组在对照组基础上结合尼可地尔治疗;各治疗4周。比较两组疗效,治疗前后心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率变化,治疗前后血管内皮功能和心功能变化及不良反应。结果 观察组总有效率(92.96%)高于对照组(77.46%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗前,两组患者心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组上述指标均较治疗前降低,但观察组治疗后心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗前,两组血浆一氧化氮(NO)和内皮素-1(ET-1)水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组血浆NO水平升高,ET-1水平降低,但观察组血浆NO水平高于对照组,ET-1水平低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。治疗前,两组每搏输出量(SV)、左心室射血分数(LVEF)和左室舒张末期内径(LVEDD)比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组SV和LVEF升高,LVEDD降低,但观察组SV和LVEF高于对照组,LVEDD低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组均未发生明显不良反应。结论 尼可地尔对高龄冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者疗效良好,且可改善患者血管功能和心功能,无明显不良反应,安全性良好。
【关键词】 尼可地尔;冠心病;不稳定心绞痛;血管内皮功能;心功能
中图分类号 R541.4 文献标识码 A 文章编号 1671-0223(2023)09--04
Clinical observation of nicorandil in the treatment of unstable angina pectoris in elderly patients with coronary heart disease Ma Zhanglu. First Department of Cardiology, Juye County People's Hospital of Heze City, Heze 274900, China
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the effect of nicorandil on vascular endothelial function and cardiac function in elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris caused by coronary heart disease. Methods Totally 142 patients with unstable angina pectoris of coronary heart disease admitted by the hospital from September 2019 to September 2021 were selected as the study subjects, and they were divided into the observation group and the control group according to gender, age, NYHA classification of cardiac function and basic disease, 71 cases per group. The patients in the control group were treated with conventional therapy, while the patients in the observation group were treated with nicorandil on the basis of the control group. Each treatment lasted for 4 weeks. The curative effects of the two groups were compared, including the duration of angina pectoris, the amount of nitroglycerin and the frequency of angina pectoris before and after treatment, the changes of vascular endothelial function and cardiac function and adverse reactions before and after treatment. Results The total effective rate of the observation group (92.96%) was higher than that of the control group (77.46%), and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Before treatment, there was no significant difference in the duration of angina pectoris, the amount of nitroglycerin and the frequency of angina pectoris between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment, the above indexes in both groups were lower than those before treatment, but the duration of angina pectoris, the amount of nitroglycerin and the frequency of angina pectoris in the observation group were lower than those in the control group after treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Before treatment, there was no significant difference between the two groups in plasma nitric oxide (NO) and endothelin-1 (ET-1) levels (P>0.05). After treatment, the plasma NO level of the two groups increased and the ET-1 level decreased, but the plasma NO level of the observation group was higher than that of the control group, and the ET-1 level was lower than that of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Before treatment, there was no significant difference in stroke volume (SV), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD) between the two groups (P>0.05). After treatment, SV and LVEF increased and LVEDD decreased in the two groups, but SV and LVEF in the observation group were higher than that in the control group, and LVEDD was lower than that in the control group, with statistically significant difference (P<0.05). No obvious adverse reactions occurred in both groups. Conclusion Nicorandil has a good effect on the elderly patients with unstable angina pectoris due to coronary heart disease, and can improve the vascular function and cardiac function of the patients without obvious adverse reactions, with good safety.
【Key words】 Nicorandil; Coronary heart disease; Unstable angina pectoris; Vascular endothelial function; Cardiac function
冠心病是常见的一种疾病,其中不稳定心绞痛主要是由于暂时性心肌缺血引起胸闷、心前区疼痛等症状群[1]。调查显示,冠心病不稳定心绞痛发病率呈不断上升趋势,且容易合并心力衰竭、心律失常等,甚至可能导致死亡,严重影响患者生活质量,威胁患者生命安全[2-3]。因此,采取早期积极有效治疗冠心病不稳定心绞痛方法尤为重要[4-6]。尼可地尔具有类硝酸酯作用,用于治疗冠心病具有保护心肌作用。本研究重点探讨尼可地尔对高龄冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者的血管内皮功能和心功能影响。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选择医院于2019年9月- 2021年9月收治的冠心病不稳定心绞痛患者142例作为研究对象。参照《高龄老年冠心病诊治中国专家共识》中相关诊断标准[7]。依据组间性别、年龄、纽约心脏病协会(NYHA)心功能分级、基础疾病分为观察组71例与对照组71例。观察组男43例,女28例;年龄80~87岁,平均83.32±2.25岁;NYHA心功能分级:Ⅱ级24例,Ⅲ级37例,Ⅳ级10例;基础疾病:高血压29例,糖尿病23例。对照组男41例,女30例;年龄81~85岁,平均年龄82.96±2.15岁;NYHA心功能分级:Ⅱ级21例,Ⅲ级42例,Ⅳ级8例;基础疾病:高血压31例,糖尿病22例。两组基线资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。本研究已通过本院伦理委员会审核,且所有患者及家属知情同意。
(1)纳入标准:①NYHA分级Ⅱ~Ⅳ级;②年龄≥80岁;③入院前4周内每次发作胸痛持续时间<30min。
(2)排除标准:①急性心肌梗死及其他心脏疾病者;②胃食管反流引起胸痛、更年期综合征以及颈椎病等引起胸痛、胸闷者;③合并造血系统及肝肾异常者;④过敏体质者。
1.2 治疗方法
对照组患者入院后采取常规治疗,包括口服肠溶阿司匹林100mg/次,每日1次;口服单硝酸山梨酯片20mg/次,每日2次;口服酒石酸美托洛尔缓释片25~50mg/次,每日2次;口服阿托伐他汀钙片20mg/次,每日1次。若患者心绞痛发作,舌下含服硝酸甘油0.5mg。观察组在对照组基础上结合尼可地尔5mg/次,每日3次。两组疗程均为4周。
1.3 观察指标
(1)有效率:有效率=(显效+有效)例数/观察例数×100%。其中,显效为患者治疗后症状消失,且患者静息心电图检查恢复正常,以及患者心绞痛发作次数减少80%及以上;有效为患者治疗后症状改善,且患者静息心电图示ST段下移回升0.5mV以上,以及患者心绞痛发作次数减少50%及以上;无效为患者治疗后症状无改善,且患者静息心电图示ST段无改善,以及患者心绞痛发作次数减少50%以下。
(2)治疗前后心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率变化。
(3)血管内皮功能:分别于治疗前后抽取外周静脉血3ml,分离血清,以硝酸还原酶法测定一氧化氮(NO)含量,以放射免疫法测定内皮素-1(ET-1)含量。
(4)心功能变化:治疗前后测量心功能,包括每搏输出量(SV)、左心室射血分数(LVEF)和左室舒张末期内径(LVEDD)。
(5)不良反应:包括恶心、呕吐、头晕、头痛、耳鸣、失眠等。
1.4 数据分析方法
运用SPSS 22.0统计学软件分析处理数据,计数资料计算百分率(%),组间率比较采用χ2检验;计量资料用“均数±标准差”表示,组间均数比较采用两独立样本t检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组疗效比较
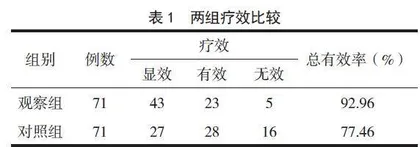
观察组总有效率(92.96%)高于对照组(77.46%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
2.2 两组患者心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率比较
治疗前,两组患者心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组上述指标均较治疗前降低,但观察组治疗后心绞痛持续时间、硝酸甘油用量和心绞痛发作频率低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
表1 两组疗效比较
组别 例数 疗效 总有效率(%)
显效 有效 无效
观察组 71 43 23 5 92.96
对照组 71 27 28 16 77.46
χ2=6.762,P=0.009。
2.3 两组血管内皮功能变化比较
治疗前,两组血浆NO和ET-1水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组血浆NO水平升高,ET-1水平降低,但观察组血浆NO水平高于对照组,ET-1水平低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表3。
2.4 两组心功能变化比较
治疗前,两组SV、LVEF和LVEDD比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);治疗后,两组SV和LVEF升高,LVEDD降低,但观察组SV和LVEF高于对照组,LVEDD低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表4。
2.5 不良反应
两组均未发生明显不良反应。