2022—2023年阜阳市食品重金属污染情况调查分析
作者: 张利 刘阳 刘景泰 张奎虎 朱美容 卜戈
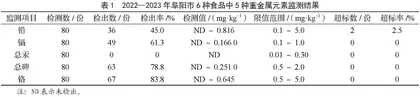
摘 要:目的:调查分析2022—2023年阜阳市食品风险监测6种食品中Pb、Cd、总Hg、总As、Cr 5种重金属污染情况,为食品安全风险监测提供数据支持。方法:采用随机采样的方法,采集阜阳市三区五县农贸市场及各类商超小麦粉、玉米粉、大米、茶叶、黄豆和蔬菜等样品,电感耦合等离子体质谱法检测,对同一重金属元素在不同样品中检出情况及不同重金属元素在相同样品中检出情况进行分析。结果:80份样品中有2份大米样品Pb超标,超标率为2.5%;5种重金属检出率依次为Cr(83.8%)>总As(78.8%)>Cd(61.3%)>Pb(45%)>总Hg(0%);茶叶样品中Cr、Pb最高检出值较高,分别为0.645 mg·kg-1和0.559 mg·kg-1,大米样品Pb、Cd、总As最高值分别为0.816 mg·kg-1、0.166 0 mg·kg-1、0.251 0 mg·kg-1,存在一定的污染风险;总Hg均未检出,5种重金属检出情况具有统计学差异,χ2=146.323,P<0.001;超标情况无统计学差异,χ2=4.401,P=0.198;结论:2022—2023年监测的80份样品中有2份大米样品Pb超标,且均来自农贸市场样品,应加强农贸市场食品安全监管力度;大米、小麦粉、玉米粉样品Pb(2份超标样品除外)、Cd、总As检出率及最大检出值偏高,虽低于标准限值,但存在一定的污染风险,茶叶中Pb、Cd、总As、Cr检出率均为100%,明显高于黄豆和蔬菜样品,未出现超标样品,总体污染状况良好,食品卫生质量相对安全,但存在污染风险,特别应加强谷物和茶叶重金属的连续监测。
关键词:食品;重金属;污染;电感耦合等离子体质谱
Investigation and Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollution in Food in Fuyang City from 2022 to 2023
Abstract: Objective: To investigate and analyze the pollution of Pb, Cd, total Hg, total As and Cr in 6 kinds of food risk monitoring in Fuyang city from 2022 to 2023, so as to provide data support for food safety risk monitoring. Method: Random sampling was used to collect wheat flour, corn flour, rice, tea, soybeans and vegetables from farmers’ markets in three districts and five counties of Fuyang city. The samples were detected by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. The detection of the same heavy metal elements in different samples and the detection of different heavy metal elements in the same samples were analyzed. Result: Among 80 samples, 2 rice samples were found to exceed the standard by Pb, and the rate of exceeding the standard was 2.5%. The detection rate of 5 heavy metals was Cr (83.8%)>Total As (78.8%)>Cd (61.3%)>Pb (45%)>total Hg (0%). The highest detectable values of Cr and Pb in tea samples were 0.645 mg·kg-1 and 0.559 mg·kg-1, respectively, while the highest detectable values of Pb, Cd and total As in rice samples were 0.816 mg·kg-1, 0.166 0 mg·kg-1 and 0.251 0 mg·kg-1, respectively, and there was a certain risk of contamination. No total Hg was detected, and there was statistical difference in the detection of 5 heavy metals, χ2=146.323, P<0.001; there were statistically significant differences in the exceedance, χ2 =4.401, P=0.198. Conclusion: Two samples of rice Pb exceeded the standard in 80 samples monitored from 2022—2023, which were from farmers’ market samples. Therefore, the supervision of food safety in farmers’ market should be strengthened. The detection rates and maximum values of Pb, Cd and total As in rice, wheat flour and corn flour samples are high, and although they are lower than the standard limits, there are certain pollution risks. The detection rates of Pb, Cd, total As and Cr in tea are 100%, which is significantly higher than that of soybean and vegetable samples, and there are no exceedance samples, so the overall pollution condition is good. The quality of food hygiene is relatively safe, but there is a risk of pollution, especially the continuous monitoring of heavy metals in cereals and tea should be strengthened.
Keywords: food; heavy metals; pollution; inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
重金属污染是全球性的重要环境污染问题之一,可通过水、空气、土壤等途径进一步污染作物,是造成食品安全风险的重要因素[1],常见的重金属有Pb、Cd、Hg、As、Cr、Al等,化学性质稳定,在环境中常以化合态稳定存在,难以降解,通过水体、土壤等途径进入食物链,进而危害人们的健康和生命安全[2]。
民以食为天,了解公众的食品安全至关重要,李恩珍等[3]研究了9类食品中8种重金属污染,发现加工水产和干菌类制品中铅、镉、铝、总汞、总砷的检出率及超标率较高;王盼盼等[4]在700份蔬菜重金属检测中发现铅、镉检出率及超标率较高,且在块茎、根茎等容易富集的部位重金属污染较为明显;王兴富等[5]发现不同茶园土壤及茶叶均存在不同程度的重金属污染;本研究通过对2022—2023年安徽省食品安全风险监测方案要求监测的80份样品中Pb、Cd、总Hg、总As、Cr 5种重金属含量进行分析,了解污染物检出水平及阜阳市食品重金属污染情况,为进一步加强食品质量市场监管、进行人群膳食暴露风险评估等提供数据支持。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 样品来源
根据2022年、2023年安徽省食品安全风险监测计划要求,采集阜阳市三区五县农贸市场及各类商超在售保质期内谷物制品、茶叶、黄豆、蔬菜商品80份,采用随机抽样的方式确保样品代表性,其中小麦粉15份、玉米粉5份、大米30份、茶叶5份、黄豆7份、蔬菜18 份。
1.1.2 仪器及试剂
赛默飞iCAP RQ电感耦合等离子体质谱仪;Millipore超纯水系统(电阻率18.2 MΩ·cm,25 ℃),安东帕Multiwave PRO全自动微波消解仪;硝酸(UP级,苏州晶瑞)。
标准物质:汞标准溶液1 000 μg·mL-1(编号234037)、As、Cd、Cr、Pb多元素标准溶液1 000 μg·mL-1(编号23D50061),均为国家有色金属及电子材料分析测试中心。
黄豆粉成分分析标准物质(编号D2010002,坛墨质检科技股份有限公司);Bi、In、Sc内标溶液100 μg·mL-1(编号23D50563,国家有色金属及电子材料分析测试中心)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 检测依据与评价依据
检测方法参照《2022年国家食品污染物和有害因素风险监测工作手册》《2023年国家食品污染物和有害因素风险监测工作手册》中食品中多元素分析的标准操作程序电感耦合等离子体质谱(Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry,ICP-MS)法。评价依据参照《食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量》(GB 2762—2017)[6]中规定茶叶中铅≤5.0 mg·kg-1,谷物及制品中铅、铬、镉、汞、砷限量分别为0.2 mg·kg-1、1.0 mg·kg-1、0.1 mg·kg-1(大米0.2 mg·kg-1)、0.02 mg·kg-1、0.5 mg·kg-1,黄豆中铅、铬、镉、汞、砷限量分别≤0.2 mg·kg-1、1.0 mg·kg-1、0.2 mg·kg-1、0.02 mg·kg-1、0.5 mg·kg-1,蔬菜中铅、铬、镉、汞、砷限量分别为0.1 mg·kg-1、0.5 mg·kg-1、0.2 mg·kg-1、0.01 mg·kg-1、0.5mg·kg-1;采用《茶叶中铬、镉、汞、砷及氟化物限量》(NY 659—2003)[7]标准中规定茶叶中铬≤5 mg·kg-1、镉≤1 mg·kg-1、汞≤0.3 mg·kg-1、砷≤2 mg·kg-1含量进行评价。
1.2.2 统计学处理
数据录入整理采用Excel 2019软件,采用SPSS 24.0软件进行χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果与分析
2.1 总体检出情况
80份样品中有2份样品检测出Pb超标,均为大米样品,超标率为2.5%;5种重金属检出率依次为Cr(83.8%)>总As(78.8%)>Cd(61.3%)>Pb(45.0%)>总Hg(0%);检出值中贡献较大的是大米和茶叶样品;总Hg均未检出,Cr、Cd、总As虽有检出,但均未超出限值。5种重金属检出情况具有统计学差异,χ2=146.323,P<0.001;超标情况无统计学差异,χ2=4.401,P=0.198;详细结果见表1。
2.1.1 6种食品中Pb的检出情况
6种食品中Pb的检出率为45%,2份样品超标,均为大米样品,检出值分别为0.816 mg·kg-1和0.509 mg·kg-1,超出谷物及制品中铅的限值0.2 mg·kg-1,样品中Pb总超标率为2.5%,大米样品超标率为6.7%;Pb的检出率中,小麦粉(100%)、玉米粉(100%)、茶叶(100%)均大于大米(36.7%)。黄豆和蔬菜样品中Pb均未检出,不同种类食品中Pb的检出情况具有统计学差异,χ2=57.650,P<0.001。具体检出结果见表2。
2.1.2 6种食品中Cd的检出情况
6种食品中Cd有不同程度的检出(玉米粉除外),总检出率为61.3%,超标率为0%。检出率大小依次为茶叶(100.0%)=黄豆(100.0%)>小麦粉(86.7%)>大米(50.0%)=蔬菜(50.0%)>玉米粉(0%),其中大米的检出值最高,为0.166 0 mg·kg-1,接近限量标准0.2 mg·kg-1,存在一定的污染风险,不同种类食品中Cd的检出情况具有统计学差异,χ2=21.639,P<0.001。具体检出结果见表3。