基于CiteSpace的2014—2023年国内牛粪堆肥发酵研究文献计量分析
作者: 王文林 刘菊莲 陈丽佳 胡登吉
摘要 日益增加的农业废弃物已成为全球环境污染的重要来源。妥善、快速地处理这些大量的废弃物对农业和生态环境的可持续发展至关重要。揭示当下牛粪堆肥发酵研究领域的研究现状,预测未来研究热点,对于未来该领域相关研究工作的深入研究方向至关重要。采用文献计量学方法,对2014—2023年Web of Science核心合集和中国知网数据库收录的牛粪堆肥发酵领域相关论文的发文特征、研究热点及其演化趋势进行定量分析,并借助CiteSpace软件进行可视化。分析结果表明:自2018年起,国外关于牛粪堆肥发酵研究的发文量显著增加,为40~85篇,远高于国内;国内发文量保持稳定;国内研究机构合作松散,以区域合作为主。国际上,中国高校为主导,研究分支多。国外研究合作强度大,核心作者发表量高,但未形成固定群;国内合作网络弱,研究分支少,多中心、分散。国外研究主题广泛,内容细致,深入探讨微生物效用和基础理论。国内研究集中于堆肥材料和工艺优化,侧重农业生产实践。农业废弃物再利用和牛粪堆肥发酵研究焦点转向微生物学机制、工艺优化和质量提升。研究结果展示了近10年来牛粪堆肥发酵的发展历程和研究热点,为相关研究挖掘出新研究方向提供了参考。
关键词 牛粪堆肥发酵;文献计量;可视化;CiteSpace
中图分类号 S-058 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2025)03-0223-06
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2025.03.045
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Bibliometric Analysis of Domestic Research on Cow Manure Composting and Fermentation from 2014 to 2023 Based on CiteSpace
WANG Wen lin1,LIU Ju lian2,CHEN Li jia3 et al
(1.Ningxia Shunbao Modern Agriculture Co.,Ltd.,Qingtongxia,Ningxia 751600; 2.Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment,Ningxia Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences,Yinchuan,Ningxia 750002; 3.Yinchuan Livestock Technology Promotion Service Center,Yinchuan,Ningxia 750002)
Abstract Increasing agricultural waste has become an important source of global environmental pollution.Proper and rapid treatment of these large amounts of waste is essential for the sustainable development of agriculture and the ecological environment.Revealing the current research status in the field of cow manure composting fermentation, and predicting future research hotspots are crucial for the future in depth research direction of related research work in this field.In this paper,the bibliometric method was used to quantitatively analyze the publishing characteristics,research hotspots and evolution trends of related papers in the field of cow manure composting and fermentation included in the Web of Science core collection and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) database from 2014 to 2023,and CiteSpace software was used for visualization.The results showed that:Since 2018,the number of publications on cow dung composting fermentation research abroad has increased significantly,from 40 to 85,which is much higher than that in China;the number of domestic publications remained stable.The cooperation of domestic research institutions is loose,mainly based on regional cooperation.Internationally,Chinese universities are dominant and there are many research branches.Foreign research cooperation is strong,and the number of core authors published is high,but no fixed group has been formed. The domestic cooperation network is weak,the research branch is few,multi center and scattered.Foreign research has a wide range of topics,detailed content,and in depth discussion of microbial utility and basic theory.Domestic research focused on composting materials and process optimization,focusing on agricultural production practices.The research focus of agricultural waste reuse and cow dung composting fermentation has shifted to microbiological mechanisms,process optimization and quality improvement.The results of this study show the development process and research hotspots of cow manure composting fermentation in the past 10 years,and provide a reference for related research to explore new research directions.
Key words Cow dung compost fermentation;Bibliometrics;Visualization;CiteSpace
基金项目 宁夏回族自治区重点研发计划(2019BCF01001)。
作者简介 王文林(1969—),男,宁夏石嘴山人,工程师,从事农业废弃物资源化利用研究。*通信作者,硕士,农艺师,从事农业废弃物资源化利用研究。
收稿日期 2024-03-27
农业废弃物是指农业生产中产生的废弃物,主要包括农作物秸秆和畜禽粪便[1]。由于人口的增加,农业废物的产生在世界范围内逐年增加。中国是世界上最大的农业废弃物生产国。畜禽粪便主要是指畜禽养殖业产生的羊粪、牛粪、鸡粪、猪粪、鸭粪等固体废弃物。禽粪便是一种主要的有机废弃物,含有作物生长发育所必需的多种营养成分,但畜禽粪便还含有许多污染物,包括氨和硫化氢等有毒气体,毒物和细菌等病原微生物[2]。据估计,我国每年有38亿t畜禽粪便,综合利用率不到60%[3]。
根据我国农业部和住建部的估算,2016年全国每年产生大量畜禽废弃物,其中高达40.0%未经回收利用就被直接排放。每年秸秆产量近9亿t,但利用率仅为77.7%。城市污泥产生量达到约3 500万 t,处置率在50.0%~70.0%;城市生活垃圾产生量达到1.8亿t[4]。牛粪富含植物所需的有机质、纤维素和氮磷钾等养分,是优质的肥料资源[5]。然而,未经处理的牛粪直接施用,其肥效利用率较低,并可能引发烧苗和病虫害的问题[6]。目前,堆肥发酵技术是处理牛粪的主要方式[7]。堆肥发酵是通过微生物的降解作用,牛粪中的纤维素、木质素等复杂成分被转化为植物易于吸收的养分;同时,微生物活动产生的高温能有效杀死病原体和害虫卵,实现畜禽粪便的无害化处理[8-9]。
为了深入了解牛粪堆肥发酵领域的研究进展及未来趋势,该研究采用了文献计量学的方法,系统性地检索了中国知网数据库 CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure)以及 WOS (Web of Science)核心文献数据库中2014—2023年的相关文献。利用数据库自带的分析工具,并借助陈超美团队开发的 CiteSpace 6.2.R6(64 bit)可视化分析软件,对全球范围内的牛粪堆肥发酵研究进行了全面的梳理和深入的分析,以期揭示该领域的研究现状、前沿动态以及我国在该领域的研究情况和发展趋势,提供有价值的参考和借鉴,推动牛粪堆肥发酵领域的持续发展。
1 数据来源
该研究所用文献数据主要以CNKI和WOS核心合集数据库作为中英文文献来源。在CNKI高级检索模式下主题词为“牛粪+堆肥+发酵”,选取同义词扩展,时间范围为2014—2023年,选择文献类型为“学术期刊”,检索时间截至 2023年12月31日,共检索到200篇文献,将其以“Refworks”格式导出;外文数据选自 WOS 核心合集数据库,检索主题为TS= “Cattle Manure” OR “Composting” OR “Aerobic Fermentation”,引文索引选择:Web of Science Core Collection(核心数据集);时间跨度为2014—2023年,选择文献类型为“Article”,检索时间截至 2023年12月31日,共检索到521篇文献,将其以“.txt”的格式导出。
该研究运用了CiteSpace 6.2.R6软件,对2014—2023年的数据进行了深入分析。对于CNKI数据库,时间切片的长度设定为每2年(Slice length=2),而对于WOS数据库,时间切片的长度设定为每4年(Slice length=4)。在参数选择上,遵循了 Top 25 per slice 的准则,即从每个时间切片中选取排名前25的数据,以生成最终的网络结构[10]。为了全面解析牛粪堆肥发酵领域的相关文献,笔者进行了关键词的时间轴聚类分析、关键词共现分析以及突现词分析等多维度汇总分析。通过这些分析方法,绘制了可视化的知识图谱,从时间发展的角度揭示技术研究的发展轨迹和热点趋势。
2 结果与分析
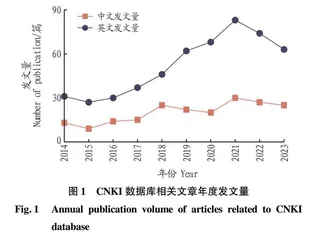
2.1 牛粪堆肥发酵研究年度发文量统计
年度发文量可以反映一定时间内某个研究领域的整体状况,能够客观反映该领域的发展过程和研究规律[11]。该研究利用OriginPro 2023b软件将所导出的文献进行统计分析,绘制出2014—2023年国内外牛粪堆肥研究的年度发文量(图1)。由图1可知,WOS数据库的牛粪堆肥研究的年度发文量在2015—2021年呈明显的增长趋势,说明在此期间,牛粪堆肥研究在国际上被广泛关注,2021年后,国际上关于牛粪堆肥研究的年度发文量略有下降;CNKI数据库在2014—2021年年度发文量处于波动上升的增长趋势;2018年后,年度发文量始终维持在20~30篇;2021年最高,为30篇。总体而言,国际上关于牛粪堆肥发酵的研究仍是一个研究热点,受到学者们广泛的关注与研究,并具有很大的研究空间,而国内预计仍然处于一个稳定增长的状态。