生物炭肥对土壤理化性质及马铃薯抗病性的影响
作者: 张天华 杨树琼 杨文兴 阮兴权
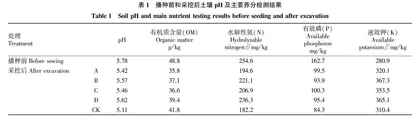
摘要 为验证生物炭肥对东川“红土地”土壤理化性质及马铃薯抗病性的影响,采用塘施和墒面撒施2种方式开展生物炭肥在马铃薯上的应用效果研究。结果显示,播种前施用生物炭肥可显著减缓马铃薯种植后土壤pH的下降,加速土壤有机质的降解,减缓土壤中水解性氮和有效磷含量的下降,显著增加土壤速效钾含量,提高马铃薯茎粗和植株覆盖度,显著提高马铃薯抗晚疫病、青枯病和疮痂病能力,显著提高马铃薯单株结薯数、单薯均重、单株产量、产量。施用2 000 kg/hm2的生物炭肥,采收后pH降幅比CK减少76.12%,有机质降解率比CK提高34.29%,水解性氮含量降幅比CK少74.72%,速效钾增加量是CK的2.85倍,对马铃薯晚疫病的防效为51.18%,马铃薯产量为37.02 t/hm2;塘施1 000 kg/hm2的生物炭肥有效磷含量降幅比CK低20.41%,对青枯病和疮痂病的防效分别为60.38%和54.78%。由此可知,生物炭肥用量越高越有利于土壤理化性质改良、提高马铃薯抗晚疫病能力和产量;将生物炭肥塘施更有利于提高马铃薯抗青枯病和疮痂病能力。
关键词 生物炭肥;马铃薯;土壤理化性质;抗病性
中图分类号 S144 文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2024)02-0147-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.02.033
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Effects of Biochar Fertilizer on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Potato Disease Resistance
ZHANG Tian-hua1, YANG Shu-qiong2, YANG Wen-xing3 et al
(1.Dongchuan Plant Protection and Quarantine Station,Kunming, Yunnan 654100;2.Dongchuan Economic Crop Technology Promotion Station,Kunming, Yunnan 654100;3.Dongchuan Agricultural Technology Extension Center,Kunming, Yunnan 654100)
Abstract In order to verify the effect of biochar fertilizer on the physical and chemical properties of Dongchuan ‘red soil’ and the disease resistance of potatoes, the application effect of biochar fertilizer on potatoes was studied by pond application and soil moisture spraying.The results showed that the application of biochar fertilizer before sowing could significantly slow down the decline of soil pH after potato planting, accelerate the degradation of soil organic matter, slow down the decline of the content of hydrolytic nitrogen and available phosphorus in soil, significantly increase the content of soil available potassium, improve the stem diameter and plant coverage of potato, significantly improve the ability of potato to resist late blight, bacterial wilt and scab, and significantly increase the number of tubers per plant, average weight of per plant, yield of per plant and yield.When 2 000 kg/hm2 biochar fertilizer was applied, the pH value decreased by 76.12% compared with CK after harvest, the organic matter degradation rate increased by 34.29% compared with CK after the biochar fertilizer increased the organic matter content, the hydrolytic nitrogen content decreased by 74.72% less than CK, the increase of available potassium was 2.85 times of CK, the control effect against potato late blight was 51.18%, and the potato yield was 37.02 t/hm2.The effective phosphorus content of 1 000 kg/hm2 biochar fertilizer applied in pond was 20.41% lower than that of CK, and its control effects on bacterial wilt and scab were 60.38% and 54.78% respectively.The higher the amount of biochar fertilizer used, the better the soil physical and chemical properties, the higher the potato yield and the better ability to resist late blight;the application of biochar fertilizer in pond was more beneficial to improve the resistance of potato to bacterial wilt and scab.
Key words Biochar fertilizer;Potato;Physical and chemical properties of soil;Disease resistance
作者简介 张天华(1976—),男,云南昆明人,高级农艺师,从事植保植检及农业技术推广工作。
收稿日期 2023-01-11
东川区位于昆明市最北端,辖6镇2街道1乡,土地面积1 865.8 km2,常住人口26.07万,户籍人口31.6万,世居少数民族主要有彝、回、布依和苗族等,是革命老区、国家老工业基地、资源型城市、国家重点生态功能区、国家乡村振兴重点帮扶县。境内海拔695~4 344 m
,可耕地面积2.8万hm2,适合种植马铃薯的面积6 666.67 hm2,马铃薯常年种植面积约为3 333.33 hm2,平均单产12 000~37 500 kg/hm2,鲜薯总产量7.5万t,占东川区种植业的11.08%[1],得天独厚的土壤、植被等自然条件使得东川区马铃薯品质优异,市场销量和价格较高,马铃薯产业已成为东川区脱贫攻坚和乡村振兴的支柱产业。
由致病疫霉(Phytophthora infestans)引起的马铃薯晚疫病[2]是马铃薯生产中主要流行性和毁灭性病害, 导致马铃薯茎叶死亡和块茎腐烂,造成巨大的产量损失[3];由茄科劳尔氏菌(Ralstonia solanacearum)引起的马铃薯青枯病[4]是一种毁灭性的细菌性土传病害,防治十分困难,是世界公认的马铃薯第二大病害,其重要性仅次于晚疫病;造成云南马铃薯疮痂病的病原链霉菌超过10种[5],由于马铃薯疮痂病主要危害块茎,导致薯块质量下降,严重影响马铃薯的经济价值[6]。
生物炭肥是一种新型的环境友好型肥料,能够影响土壤pH[7]、有机质含量[8-9]、氮磷钾含量[7-8]、土壤保水性[10-11]、孔隙度[10-11]、容重[10-11]、土壤酶活性[12]、土壤微生物群落[12-13]等理化性状,在土壤质地改良和修复方面具有较大潜力,已成为耕地土壤改良和修复研究的热点。刘志华等[7]研究显示,足量水分条件下,5%生物炭添加和10%生物炭添加的土壤pH显著增加,干旱条件下生物炭对土壤速效养分的影响与施用量有关,添加1%生物炭对土壤速效养分含量无显著影响,添加10%生物炭的土壤速效氮、速效磷显著降低,速效钾含量升高;任少勇[8]研究显示,等量氮磷钾条件下,0~40 cm土层施炭基肥处理的土壤有机质、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾含量和变化值的平均值显著高于化肥处理;苏彩霞等[9]研究显示,BFG(炭基)有机肥能提高土壤有机碳含量,促进营养元素的释放;焦瑞枣等[10]研究显示,马铃薯田施炭基肥后土壤容重的降幅和孔隙度的增幅明显高于化肥处理,块茎增长期和成熟收获期的土壤养分含量均高于化肥处理;张国辉等[11]研究显示,生物炭可显著提高马铃薯耕层土壤田间持水量和含水量,降低土壤容重,增加孔隙度,提高土壤水分利用效率,实现高产;屠娟丽等[12]研究显示,施用200 g/株的秸秆生物炭,根区土壤过氧化氢酶、脲酶、多酚氧化酶和蔗糖酶活性以及土壤微生物的 AWCD 值(平均吸光值)、丰富度指数、优势度指数和均匀度指数均有所增加;黄修梅等[13]研究显示,各生物炭处理均降低了土壤真菌丰度,生物炭处理有利于提高子囊菌门的丰度,降低担子菌门和接合菌门的丰度。生物炭肥还能提高马铃薯产量,提高淀粉、蛋白质及干物质含量[14-16]。苏彩霞等[9]研究发现施用 BGF有机肥能有效降低马铃薯早疫病、炭疽病和疮痂病的发病程度;生物炭肥施用对马铃薯晚疫病和青枯病的影响则鲜见报道。
笔者开展田间随机区组试验,研究生物炭肥对东川“红土地”土壤理化性质及马铃薯抗病性的影响。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验地概况
试验地块位于昆明市东川区红土地镇花沟村,103.2188°E,26.1363°N;海拔2 200 m。试验地块地势平坦,土壤为红壤土,偏酸性,肥力适中。
1.2 试验材料 试验品种为青薯9号。
生物炭肥,作物秸秆炭化而成,其中含有0.2亿/g的霍尔德伯克氏菌,昆明保腾生化技术有限公司提供。
1.3 试验方法 采用随机区组设计,各处理3次重复;小区面积48 m2(1.2 m×20 m×2),每小区2垄,每垄种植2行马铃薯,每小区种植228株。共5个处理,4个生物炭肥处理和1个空白对照;处理A,按750 kg/hm2的量塘施生物炭肥;处理B,按1 500 kg/hm2的量塘施生物炭肥;处理C,按100 g/m2(1 000 kg/hm2)的量墒面撒施生物炭肥;处理D,按200 g/m2(2 000 kg/hm2)的量墒面撒施生物炭肥;处理CK,不施用生物炭肥。