不同大小蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性研究
作者: 董飞 齐宇 王烨楠 马蕾 吕晓惠 张冀华 朱娇
摘要 以“16136”为试材,调查8.3和11.6 cm蝴蝶兰催花后的开花性状,并采用 Excel 2016 进行数据整理,SPSS 19.0进行统计分析。研究不同大小蝴蝶兰开花性状之间的相关性,以期建立一个外观质量鉴定标准。结果表明,8.3和11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花朵数、花纵径、花梗长、花序长间的差异均达极显著水平;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径、花梗数呈极显著和显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.392 3**和0.300 5*;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的花纵径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径、花梗数呈极显著和显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.543 4**和0.382 5*;且8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径和花纵径对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花朵数具有负效应;8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花梗长和花序长对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花纵径具有负效应;8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花梗长和花梗数对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花序长具有负效应;8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花梗长、花序长和花梗数对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花朵数具有正效应;8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花朵数、花横径、花序长和花梗数对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花序长具有正效应,且花朵数对花序长的正效应最大;8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花朵数和花梗数对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花梗数具有正效应。
关键词 蝴蝶兰;开花性状;相关性分析
中图分类号 S 682.31 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2024)20-0045-03
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.20.010
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Correlation Study on Flowering Characters of Phalaenopsis aphrodite of Different Sizes
DONG Fei, QI Yu ,WANG Ye-nan et al
(Institute of Leisure Agriculture, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences / Key Laboratory of East China Urban Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs / Shandong Engineering Research Center of Ecological Horticultural Plant Breeding, Jinan, Shandong 250100)
Abstract Using “16136” as the test material, the flowering characteristics of 8.3 and 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite were investigated. Excel 2016 was used for data sorting and SPSS 19.0 was used for statistical analysis. The correlation between flowering characters of different sizes of Phalaenopsis aphrodite was studied in order to establish a standard for identification of appearance quality. The results showed that the differences in flowering traits between 8.3 and 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite were extremely significant in terms of flower number, longitudinal diameter, pedicel length, and inflorescence length;the transverse diameter of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite and the transverse diameter and number of flower stems of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite were highly significant and significantly positively correlated, with correlation coefficients of 0.392 3** and 0.300 5**, respectively;the longitudinal diameter of the 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite was highly significantly and positively correlated with the transverse diameter and number of pedicels of the 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite, with correlation coefficients of 0.543 4** and 0.382 5**, respectively;moreover, the transverse and longitudinal flower diameters of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a negative effect on the number of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite;the stem length and inflorescence length of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a negative effect on the longitudinal diameter of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite;the pedicel length and number of pedicels of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a negative effect on the inflorescence length of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite;the stem length, inflorescence length, and stem number of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a positive effect on the number of flowers in 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite;the number of flowers, transverse diameter, inflorescence length, and number of pedicels of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a positive effect on the inflorescence length of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite, and the number of flowers had the greatest positive effect on inflorescence length;the number of flowers and flower stems of 8.3 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite had a positive effect on the number of flower stems of 11.6 cm Phalaenopsis aphrodite.
Key words Phalaenopsis aphrodite;Flowering character;Correlation analysis
蝴蝶兰(Phalaenopsis aphrodite)为兰科蝴蝶兰属植物,属附生兰,又称蝶兰[1]。蝴蝶兰的花朵艳丽娇俏,颜色丰富明快,观赏期长,花朵数多,既能净化空气又可作盆栽观赏,还可用作切花、贵宾胸花、新娘捧花、花篮插花的高档素材[2]。在中国台湾、菲律宾、泰国、马来西亚、印度尼西亚等地都有分布,北方主要依靠温室进行栽培种植,是目前国际上销量最高的高档盆花[3]。近几年,随着蝴蝶兰产业的迅猛发展,更是稳居年宵花首位[4]。
蝴蝶兰生长缓慢,育种周期长,育种成本高。为了能够缩短育种周期,从5.0 cm或者8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的开花性状预测11.6 cm成熟蝴蝶兰开花特性,提前掌握开花状态,提前进行选择和淘汰,不仅能够缩短育种周期还能节约成本、提高育种效率。目前,关于蝴蝶兰的研究主要集中在杂交育种[5-7]、组培快繁[8-10]、栽培技术[11-12]、花期调控[13-14]等方面,对不同大小蝴蝶兰开花性状之间的相关性研究很少。笔者以蝴蝶兰“16136”为试材,调查8.3和11.6 cm蝴蝶兰催花后的开花性状,分析2组数据之间的相关性,以期建立一个快速简洁的花朵质量性状的预测标准,早期预测开花性状,为缩短育种周期、提高育种效率奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
以蝴蝶兰“16136”为试验材料,在山东省农业科学院连栋温室进行。
1.2 试验方法
在温室中选择300棵长势一致、性状优良的5.0 cm“16136”蝴蝶兰种苗,且这些蝴蝶兰已在温室中生长180 d,选择100棵5.0 cm蝴蝶兰测定其形态指标。测量完毕后将300棵蝴蝶兰从5.0 cm营养钵换到8.3 cm营养钵,生长180 d后,选择100棵8.3 cm蝴蝶兰测定其形态指标。测量完毕后将300棵蝴蝶兰从8.3 cm营养钵换到11.6 cm营养钵,生长180 d后,选择100棵11.6 cm蝴蝶兰测定其形态指标。蝴蝶兰种苗在白天(30±3)℃、夜晚(25±3)℃、湿度(70±5)%的环境中生长。
1.3 测定项目与方法
用游标卡尺和直尺测定所有植株的开花性状,包括花梗长、花序长、花朵横径、花朵纵径、花朵数、花梗数等。当蝴蝶兰有2个及以上花梗时,花梗长为几个花梗长的总数,花序长也是几个花序长的总和。
1.4 数据处理与分析
测定数据采用 Excel 2016 进行数据整理,SPSS 19.0进行统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 不同大小蝴蝶兰的开花性状
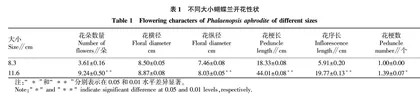
由表1可知,随着蝴蝶兰形态的不断增加,花朵数量、花横径、花纵径、花梗长、花序长不断增大。8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花时只有1.00个花梗,11.6 cm开花时出现了1.39个花梗。通过对2组数据进行t检测发现,除花横径外,11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的其他开花性状与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰均有显著或极显著差异。其中,2组数据在花朵数、花纵径、花梗长、花序长间的差异达极显著水平。
2.2 不同大小蝴蝶兰开花性状之间的相关性分析
通过对11.6 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状和8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性进行分析发现,11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花朵数与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X2>X1>X4>X3>X6>X5,但未均达显著水平。11.6 cm 蝴蝶兰花横径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X2>X6>X4>X5>X3>X 且11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径、花梗数呈极显著和显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.392 3**和0.300 5*。11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花纵径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X2>X6>X4>X5>X3>X 且11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的花纵径与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的花横径、花梗数呈极显著和显著正相关,相关系数分别为0.543 4**和0.382 5*。11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花梗长与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X2>X4>X3>X1>X6>X5,但均未达显著水平。11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花序长与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X2>X4>X6>X3>X5>X 但均未达显著水平。11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花梗数与8.3 cm蝴蝶兰开花性状的相关性依次为X4>X2>X3>X1>X5>X6,但均未达显著水平(表2)。
2.3 逐步回归分析
以11.6 cm蝴蝶兰的开花性状为因变量,以8.3 cm蝴蝶兰的开花性状为自变量进行逐步回归。11.6 cm 寸蝴蝶兰花朵数通过逐步回归,建立以X2、X3、X4、X5、X6为自变量的最优回归模型Y1=151.59-21.68X2-0.89X3+1.66X4+2.76X5+0.59 X6,R2为0.64;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花横径通过逐步回归,建立以X4、X5、X6为自变量的最优回归模型Y2=-2.32+0.43 X4+0.47 X5+0.57 X6,R2为0.78;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花纵径通过逐步回归,建立以X2、X4、X5为自变量的最优回归模型Y3=5.30+1.51X2-0.38X4-0.50X5,R2为0.50;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花梗长通过逐步回归,建立以X1、X5、X6为自变量的最优回归模型Y4=87.05+26.94X1-25.29X5+11.10X6,R2为0.45;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花序长通过逐步回归,建立以X1、X2、X4、X5、X6为自变量的最优回归模型Y5=133.83-9.66X1+15.23X2-8.82X4-7.39X5-3.87X6,R2为0.88;11.6 cm蝴蝶兰花梗数通过逐步回归,建立以X1、X5、X6为自变量的最优回归模型Y6=1.92+0.60X1-0.34X5-0.38X6,R2为0.48。