贵州梵净山世界自然遗产地旅游线路植物资源探讨
作者: 刘明智 陈明霞 袁波 罗家勋 谭善财
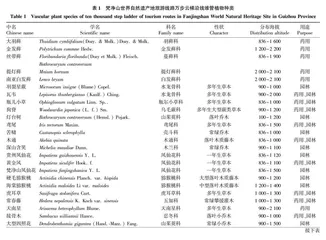
摘要 [目的]探索梵净山世界自然遗产地的原始森林植物物种。[方法]2019年5月在旅游淡季时沿旅游线路的万步云梯从步梯0步(鱼坳,海拔836 m)至金顶蘑菇石(海拔2 318 m),对总海拔跨度1 482 m的步梯沿途视野20 m处维管植物物种进行考察并拍照,室内结合《中国植物志》等资料鉴定植物物种。[结果]梵净山世界自然遗产地有穗花杉、伯乐树、粗榧、华西花楸、瓶尔小草、金发藓等植物达100种之多,并且总海拔跨度1 482 m的梵净山世界自然遗产地植被垂直带谱明显,其中836~1 300 m处为常绿阔叶林,第三纪古老孑遗的长柄水青冈群落分布在海拔1 114 m处;1 300~1 900 m处为三峡槭、贵州青冈、亮叶水青冈和米心水青冈等组成的常绿落叶阔叶混交林;1 900~2 100 m处为亮叶水青冈、多脉青冈等为优势种的落叶阔叶林,结构完整、自然更替良好的贵州青冈群落分布在海拔2 031 m处;2 100~2 200 m为雷山杜鹃、大钟杜鹃、吊钟花等杜鹃花科植物和木樨科的川滇蜡树等亚高山杜鹃矮林,林下层为箭竹、玉簪等草本,2 200~2 318 m为亚高山灌丛草甸,由紫药红荚蒾、西康绣线菊等形成的灌丛及玉山针蔺兰、黄毛草莓等草丛,并有箭竹分布于该植被带。海拔2 000 m以上苔藓植物分布丰富,主要有南亚白发藓、提灯藓、大羽藓、金发藓等。[结论]在贵州梵净山世界自然遗产地有着保存完好的亚热带原始常绿及落叶阔叶林,植被覆盖率在90%以上,植被垂直带谱明显。
关键词 梵净山;万步云梯;植物种类;植被
中图分类号 S 788.2 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2023)07-0126-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2023.07.030
Study on Plant Resources of Tourism Routes in Fanjingshan World Natural Heritage Site in Guizhou Province
LIU Ming-zhi1,CHEN Ming-xia2, YUAN Bo1 et al
(1.School of Agriculture, Tongren Vocational and Technical College, Tongren, Guizhou 554300; 2. College of Humanities, Tongren University, Tongren, Guizhou 554300)
Abstract [Objective] To explore the plant species of the original forest in Fanjing Mountain in the World Natural Heritage Site. [Method]In the off-season of tourism in May 2019, plant species were examined and photographed at 20 m along the total elevation span of 1 482 m along the ladder from 0 step (Yuao, elevation 836 m) to JindingMoshi (elevation 2 318 m). Plant species were identified by combining the data of Flora of China and other materials. [Result] The results showed that there were over 100 plants species in World Natural Heritage Site in Fanjingshan, such as Ametotaxus argotaenia (Hance) Pilger., Bretschneidera sinensis Hemsl., Cephalotaxus sinensis (Rehd. et Wils.) Li., Sorbus wilsoniana Schneid, Ophioglossum vulgatum Linn. Sp.,Floribundaria floribunda(Dozy et Molk.) Fleisch..The altitudinal spectrum of vegetation was obvious in World Natural Heritage Site in Fanjingshan with a total altitude span of 1 482 m.The evergreen broad-leaved forest was located at 836-1 300 m altitude, and the ancient tertiary relict community of Cyclobalanopsis pedunculata was distributed at 1 114 m altitude.
An evergreen deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest composed of Acer wilsonii,Cyclobalanopsis argyrotricha, Fagus lucida and Fagus engleriana. et was located at a distance of 1 300 m to 1 900 m; There were deciduous broad-leaved forests with dominant species such as Fagus lucida and Cyclobalanopsis multinervis etc. at 1 900 m to 2 100 m. Cyclobalanopsis argyrotricha community which had a complete structure and good natural replacement, is distributed at an altitude of approximately 2 031 m.
Subalpine rhododendron scrub forest distrubuted 2 100-2 200 m composed Ericaceae and Oleaceae, Rhododendron leishanicum,Rhododendron ririei, Enkianthus quinqueflorus et, Ligustrum delavayanum, there were Fargesia spathacea, Hosta plantaginea;2 200-2 318 m was subalpine shrub meadow, shrub layer was composed by Spiraea schneideriana and Viburnum erubescens et, meadow was composed by Eulaliopsis binata,Fragaria nilgerrensis et, and Fargesia spathacea distributed in the vegetation belt. Bryophyte was abundant above 2 000 m, they are Lenco bryum,Mnium hornum,Thuidium cymbifolium, Polytrichum commne. [Conclusion]There were a well-preserved subtropical original evergreen and deciduous broadleaved forest in The World Natural Heritage Site in Fanjingshan, Guizhou, the vegetation coverage rate was more than 90%, the vertical spectrum of vegetation was obvious.
Key words Fanjing Mountain;Ten thousand step ladder; Plant species;Vegetation
基金项目 铜仁市科技计划项目(铜市科研〔2017〕23号)。
作者简介 刘明智(1969—),男,苗族,湖南绥宁人,副教授,博士,从事植物学和生态学研究。
收稿日期 2022-05-28
贵州梵净山位于黔东铜仁市的江口县、印江县和松桃县3县交界处,系武陵山脉最高峰,被誉为贵州第一山,1986年被列为我国首批国家级自然保护区,是一个以常绿阔叶林、落叶阔叶林为主的森林生态系统[1],于2013年列为世界自然遗产提名地,不但具有丰富的生物多样性和完整性,还有着壮丽的自然景观和亚热带生态的珍稀动植物。联合国教科文组织于2018年7月将其列入世界自然遗产名录,成为我国第13处及世界第53处世界自然遗产,更是旅游观光避暑之圣地。梵净山地区自第四纪以来一直处于温暖湿润的环境中,成为多种植物繁衍生存处,是一个罕见的生物资源基因库[2]。梵净山是在酸性砂岩上发育着典型的中亚热带常绿、落叶阔叶混交林[3],林中有梵净山冷杉(Abies fanjingshanensis)、伯乐树(Bretschneidera sinensis Hemsl.)、红豆杉(Taxus wallichiana var.mairei)等多种珍稀植物[4],且梵净山保护区内植被保存完好,原生性强,植被垂直分异明显[5],在不同海拔地带,不同类型的植物群落显现出不同的森林景观[6]。地理位置和地貌的独特性,兼之有利的气候条件,再者极少的人为活动干扰使得梵净山的生物多样性极其丰富,仅高等植物就达3 000余种,且森林覆盖率达90%[7]。长期以来,国内学者对梵净山自然保护区的种子植物种类[8]、种子植物区系[9]、蕨类植物种类[10]、蕨类植物区系[11]及梵净山旅游线路苔藓植物与药用苔藓资源[12]等方面进行了调查与研究,而对梵净山的旅游线路沿途的维管植物进行调查鲜见研究。笔者开展梵净山世界遗产地万步云梯旅游线路沿途植物资源及植被类型探讨,尤其是种子植物资源研究,旨在为梵净山世界遗产地的旅游与生态环境保护、植物资源可持续性利用及植被永续性建设管理提供一定的理论基础和参考依据。
1 研究区自然概况
梵净山世界自然遗产地位于贵州省东北部铜仁市东挨湖南湘西,西抵重庆秀山,地理位置108°45′55″~108°48′30″E,27°49′50″~28°01′30″N,既是武陵山主峰,又是乌江与沅江的分水岭。梵净山山体庞大、地势高耸,凤凰山为其最高峰,海拔为2 572 m,金顶为次峰,海拔为2 493.14 m,周边区域则整体以低中山、低山喀斯特地貌景观类型为主,山体垂直高差达2 000 m,总面积为567 km2[13]。居于我国亚热带中心的梵净山,年均温6~17 ℃,年降水量1 100~2 600 mm,年均相对湿度80%以上,属于明显的中亚热带季风山地湿润气候,同时兼具山地垂直典型气候,属于我国热带、亚热带生物区系向温带生物区系的生态交错区[14];土壤为典型森林土壤,其中以山地黄壤和暗黄棕壤分布面积最多,并且土壤表层腐殖质含量高,枯枝落叶干物质达40~80 t/hm2[13];土壤垂直带谱明显,由山麓到山顶土壤类型依次为山地黄红壤、山地黄壤、山地暗黄棕壤、高山草甸土[15]。复杂多样的地形地势、充沛的水热条件与良好的土壤环境不但造就了梵净山植物资源非常丰富,仅种子植物达1 800种之多[13],并且有丰富的植被类型,包括马尾松(Pinus massoniana Lamb.)和杉木(Cunninghamia lanceolata(Lamb.)Hook.)等针叶林,苦槠(Castanopsis sclerophylla(Lindl.)Schott.)等为优势种的常绿阔叶林,贵州青冈(Cyclobalanopsis argyrotricha(A.Camus)Chun et Y.T.Chang)等常绿阔叶林与米心水青冈(Fagus engleriana Seem.)等落叶阔叶混交林,光叶水青冈(Fagus lucida Rehd.et Wils.)等落叶阔叶林及楠竹(Phyllostachys pubescens Mazel ex H.de Leh.)林和亚高山灌丛草甸等植被类型,植被覆盖度达80%以上,明显高于周边植被稀疏的喀斯特地区[16]。梵净山不仅生物多样性较高,而且有俗称“中国鸽子树”的珙桐(Davidia involucrata Bail.)、穗花杉(Ametotaxus argotaenia(Hance.)Pilger.)、鹅掌楸(Liriodendron Chinense(Hemsl.)Sarg.)等众多特有植物、珍稀濒危植物[16]。