黄河口大闸蟹不同可食部分营养分析
作者: 成慧中 王志忠 张琦 赵金山 王新军 胡斌 朱永安 周凯
摘要 [目的]分析黄河口大闸蟹(Eriocheir sinensis)雌雄蟹肌肉、肝胰腺和性腺等不同可食部位的营养成分和品质。[方法]比较雌雄蟹肌肉、肝胰腺和性腺等可食部分的常规营养成分、矿物质、氨基酸和脂肪酸含量。[结果]黄河口大闸蟹性腺中蛋白质和肝胰腺中脂肪的含量最高,雌蟹性腺和肝胰腺中蛋白质以及可食部分脂肪含量均高于雄蟹;所测得的7种矿物质元素在雌雄蟹不同可食部分的含量有明显差异,钙、锰含量以雄蟹性腺中最高,镁、磷、锌含量以雌蟹性腺中最高,铁、铜含量以雌蟹肝胰腺中最高;检测出的19种氨基酸中以谷氨酸含量最高,其次是天冬氨酸,可食部分中总氨基酸、必需氨基酸、半必需氨基酸、鲜味氨基酸和非必需氨基酸含量均以性腺中最高,可食部分中支链氨基酸较高;共检测出30种脂肪酸,包括13种饱和脂肪酸(SFA)、7种单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA)和10种多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA),可食部分中SFA、MUFA、PUFA、∑PUFAn-3、∑PUFAn-6的含量及脂肪酸总量均以肝胰腺中最高,且雌蟹高于雄蟹,可食部分中C22:6n-3(DHA)含量和DHA/EPA值较高,可食部分的脂肪酸致动脉粥样硬化指数(AI)和致血栓指数(TI)较低,均值分别在0.24~0.55和0.03~0.44。[结论]黄河口大闸蟹可食部分营养较为丰富,具有一定的保健作用。
关键词 黄河口大闸蟹;肌肉;肝胰腺;性腺;营养成分;品质评价
中图分类号 TS 201.4 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2023)15-0166-06
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2023.15.041
Nutritional Analysis of Different Edible Parts of Eriocheir sinensis in the Yellow River Estuary
CHENG Hui-zhong1, WANG Zhi-zhong1,ZHANG Qi2 et al
(1.Shandong Fresh Water Fisheries Research Institute,Jinan,Shandong 250013;2.Dongying Kenli Fisheries and Fishing Port Service Center,Dongying,Shandong 257500)
Abstract [Objective] To analyze the nutritional components and quality of different edible parts such as muscle, hepatopancreas and gonad of male and female Eriocheir sinensis of Yellow River Estuary.[Method] The study compared the contents of conventional nutritional components, minerals, amino acids and fatty acid of the edible parts of male and female Eriocheir sinensis, such as muscles, hepatopancreas and gonads.[Result]The contents of protein in gonad and fat in hepatopancreas were the highest, the content of protein in the gonads and hepatopancreas and edible fat of female Eriocheir sinensis were higher than that of male Eriocheir sinensis in the Yellow River Estuary. It was deteceted seven mineral elements which were significantly different in edible parts of male and female crabs. The contents of Ca and Mn in male crabs’ gonads, the contents of Mg, P and Zn in female crabs’ gonads, and the contents of Fe and Cu in hepatopancreas of female crabs were the highest. Among the 19 amino acids detected, the content of glutamic acid was the highest, followed by aspartic acid. The content of total amino acids (TAA), essential amino acids (EAA), semi-essential amino acids (SEAA), delicious amino acid (DAA) and no-essential amino acids (NEAA) in gonad were the highest, and branched-chain amino acid in the edible part was the highest.It was totally detected 30 fatty acids, including 13 saturated fatty acids (SFA), 7 monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA) and 10 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). The contents of SFA, MUFA, PUFA, ∑PUFAn-3, ∑PUFAn-6 and total fatty acids in the edible part of the crab were the highest in the hepatopancreas,and female crabs were higher than male crabs. The contents of C22:6n-3(DHA) and DHA/EPA in the edible part of the crabs were higher,and the fatty acid arteriosclerosis index (AI) and thrombotic index (TI) of the edible fraction were lower, with the mean values of 0.24-0.55 and 0.03-0.44, respectively.[Conclusion] The edible part of Eriocheir sinensis in the Yellow River Estuary was rich in nutrition and had certain health function.
Key words Eriocheir sinensis in the Yellow River Estuary;Muscle;Hepatopancreas;Gonad;Nutritional components;Quality evaluation
黄河口大闸蟹,学名中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheir sinensis),又称河蟹,隶属节肢动物门(Arthropoda)甲壳纲(Crustacca)十足目(Decapoda)方蟹科(Grapsidae)绒螯蟹属(Eriocheir)[1],生长于黄河口附近,是山东省东营市的名优水产品[2]。黄河口大闸蟹2008年被认定为全国农产品地理标志产品,是山东省十大渔业品牌,2020年品牌价值达26.12亿元,2022年成为第一批“好品山东”品牌。
东营市地处山东省东北部、黄河入海口,因其气候温和、水源充沛、水草丰茂、具有优质的生态环境,适宜黄河口大闸蟹生长繁殖,其中,垦利区的生态养殖面积达6.67万hm2,是东营市养殖总面积最大、产量产值最高的区域。目前对不同种群河蟹生长性能、成活率、性腺发育和营养成分等方面已有研究报道,李应森等[3]、李晨虹等[4]比较了辽河和长江种群河蟹养殖阶段的生长性能的差异,赵恒亮等[5]对长江、黄河和辽河种群河蟹雌体卵巢发育和营养组成进行了比较研究,但对黄河中下游河蟹不同可食部分营养分析鲜见报道。该研究通过对黄河口大闸蟹雌蟹和雄蟹不同可食部分的营养分析与质量评价,比较雌雄蟹肌肉、肝胰腺和性腺等可食部分的常规营养成分、矿物质、氨基酸和脂肪酸含量,为黄河口大闸蟹种质资源评价、优异形状挖掘利用等相关研究提供基础资料。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
黄河口大闸蟹于2021年11月份取自东营市黄河口大闸蟹协会。随机选取蟹壳坚硬、附肢齐全、健壮有力的性成熟雄性和雌性黄河口大闸蟹,雄性个体重量为130~175 g,雌性为100~150 g。
1.2 样品制备
将采集的活体雌雄样品蟹分别用自来水冲洗后,吸干表面水分,逐只打开背腹甲,在白色瓷盘内取出其肌肉、肝胰腺、性腺等可食部分,分别装入密实袋中,在-20 ℃条件下冷冻保存备用。样品送至青岛市华测检测技术有限公司进行检测。
1.3 测定方法
黄河口大闸蟹可食部分营养成分的分析方法,蛋白质按GB 5009.5—2016规定执行,脂肪按GB 5009.6—2016规定执行,水分按GB 5009.3—2016规定执行,灰分按GB 5009.4—2016规定执行;磷按GB 5009.87—2016规定执行,铁、铜、钙、锌、锰、镁等矿物质按GB 5009.268—2016规定执行;天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、精氨酸、丙氨酸、苏氨酸、丝氨酸、甘氨酸、脯氨酸、缬氨酸、酪氨酸、蛋氨酸、赖氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、组氨酸和异亮氨酸按GB 5009.124—2016规定执行,色氨酸、牛磺酸和半胱氨酸分别参考GB/T 18246中的碱水解法、常规酸水解法和氧化酸水解法的规定执行;脂肪酸按照GB 5009.168—2016规定执行。
1.4 营养品质评价方法
1.4.1 氨基酸。
根据粮食与农业组织/世界卫生组织(FAO/WHO)(1973)建议的氨基酸评分标准模式[6]和全鸡蛋蛋白质的氨基酸模式[7],分别按以下公式计算氨基酸评分(AAS)、化学评分(CS)和氨基酸的支芳值(F值)。
AAS=测试样品中氨基酸含量/(FAO/WHO评分标准模式中同种氨基酸含量)
CS=测定样品中氨基酸含量/(全鸡蛋蛋白质中同种氨基酸含量)
F值是支链氨基酸(BCAA)与芳香族氨基酸(AAA)的比值[8],公式如下:
F=(缬氨酸+亮氨酸+异亮氨酸)/(苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸)
1.4.2 脂肪酸。
参考文献[9]计算黄河口大闸蟹脂肪酸致动脉粥样硬化指数(atherogenic index,AI)和致血栓指数(thrombogenic index,TI),公式如下:
AI=(C12:0+4×C14:0+C16:0)/(MUFA+PUFAn-6+PUFAn-3)
TI=(C14:0+C16:0+C18:0)/(0.5×MUFA+0.5×PUFAn-6+3×PUFAn-3+PUFAn-3/PUFAn-6)
式中,MUFA为单不饱和脂肪酸,PUFA为多不饱和脂肪酸。
2 结果与分析
2.1 常规营养成分
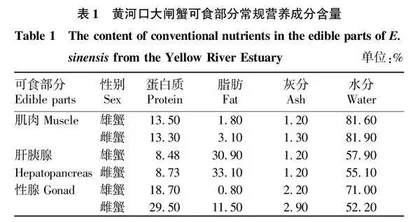
从黄河口大闸蟹可食用部分的常规营养成分(表1)可以看出,黄河口大闸蟹性腺中蛋白质含量最高,明显高于肌肉和肝胰腺中的含量,肝胰腺中蛋白质含量相对较低;雌蟹性腺和肝胰腺中蛋白质含量(29.50%和8.73%)均高于雄蟹(18.70%和8.48%)。肝胰腺中脂肪含量最高,明显高于肌肉和性腺中的含量;雌蟹不同部位可食部分的脂肪含量均高于雄蟹。肌肉中水分含量最高,均在80%以上,明显高于性腺和肝胰腺中的含量。性腺中灰分含量最高,明显高于肌肉和肝胰腺中的含量。
2.2 矿物质元素
所测得的7种矿物质元素中包括常量元素钙、镁、磷和微量元素锌、铁、铜、锰。从表2可以看出,钙、锰含量均以雄蟹性腺中最高,分别为1 080.00和3.90 mg/kg,明显高于其他含量;雄蟹肌肉中钙、锰含量均低于雌蟹。镁、磷、锌含量均以雌蟹性腺中最高,分别为762.00、3 760.00和45.90 mg/kg,明显高于其他含量。铁、铜含量均以雌蟹肝胰腺中最高,分别为207.00和8.83 mg/kg;雌蟹可食部分中铁、铜含量均高于雄蟹。
2.3 氨基酸及其评价