物维生素B<sub>1</sub>生物合成及生物强化的研究进展
作者: 孙亚丽 唐家琪 毛馨晨 王子瑞 张超 于恒秀
摘要 维生素B1是所有生物所必需的微量元素,其作为多个酶的辅因子,参与重要的细胞代谢途径。人体缺乏维生素B1会增加罹患心血管及神经失调性疾病的风险。与植物和微生物不同,人类和其他动物不能从头合成维生素B1,必须从饮食中获取。因此,研究植物中维生素的生物合成途径,并在此基础上对植物中的维生素B1含量进行生物强化具有重要意义。维生素B1合成途径中有许多酶的参与,如嘧啶合成酶(THIC)、噻唑合成酶(THI1)、硫胺素磷酸合成酶(TH1)、硫胺素单磷酸酶(TH2)和硫胺素焦磷酸激酶(TPK)等。结合相关研究,对维生素B1在植物中的生物学功能、生物合成途径及合成相关基因的功能进行总结,并介绍了通过代谢工程实现生物强化的研究进展,以期为进一步提高植物中维生素B1含量提供参考。
关键词 维生素B1;硫胺素;生物合成;生物强化;植物
中图分类号 Q946 文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2024)02-0005-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.02.002
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Research Progress on Biosynthesis and Biofortification of Vitamin B1 in Plants
SUN Ya-li, TANG Jia-qi, MAO Xin-chen et al
(Agricultural College of Yangzhou University/Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Crop Genetics and Physiology/ Key Laboratory of Plant Functional Genomics of the Ministry of Education/Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Crop Genomics and Molecular Breeding/ Jiangsu Co-Innovation Center for Modern Production Technology of Grain Crops,Yangzhou,Jiangsu 225009)
Abstract Vitamin B1 is an essential micronutrient for all living organisms. As a cofactor of many enzymes, it participates in important cellular metabolic pathways. Vitamin B1 deficiency increases the risk of cardiovascular and neurological disorders in human. Unlike plants and microbes, humans and other animals cannot synthesize vitamin B1 de novo and must acquire it from their diets. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the vitamin B1 biosynthesis pathway and to biofortify the vitamin B1 content in plants. There are many enzymes involved in the vitamin synthesis pathway, such as pyrimidine synthetase (THIC), thiazole synthetase (THI1), thiamine phosphate synthetase (TH1), thiamine monophosphatase (TH2) and thiamine pyrophosphate kinase (TPK). In this paper, the biological functions of vitamin B1 in plants, biosynthetic pathways and functions of synthesis-related genes were summarized based on the latest research progress, and the progress of biofortification through metabolic engineering was reviewed. This paper may highlight opportunities for further improving the content of vitamin B1 in plants.
Key words Vitamin B1;Thiamin;Biosynthesis;Biofortification;Plants
基金项目 江苏省自然科学基金青年项目(BK20200951)。
作者简介 孙亚丽(1998—),女,河南信阳人,硕士研究生,研究方向:水稻遗传育种。
*通信作者,教授,博士,从事水稻遗传育种研究。
收稿日期 2023-02-06
维生素B1于1926年从米糠中分离,是最早被提纯的维生素[1]。维生素B1有助于促进人类神经健康、改善情绪、增强心脏和减少胃灼热[2-3],同时维生素B1也是一种抗氧化剂[4-5]。当维生素B1摄入量不足时,往往会出现微量营养素缺乏症。若严重缺乏维生素B1,则会干扰中枢神经和循环系统,并导致脚气病[6-7]。“脚气病”是一种人类致命疾病,在以高碳水化合物为主食的国家中普遍存在[8]。
维生素B1在植物的生长发育、非生物和生物胁迫的响应中发挥着重要的作用[9]。维生素B1参与许多细胞代谢途径并作为一些重要酶的辅酶,如三羧酸循环(tricarboxylic acid cycle,TCA cycle)、己糖二磷酸途径(embden-meyerhof-parnas pathway,EMP)等[10-11]。维生素B1缺乏会导致植物新陈代谢速率减慢、呼吸作用减弱、光合作用下降、蔗糖和氨基酸残基的累积量增高。在玉米维生素B1合成缺陷的突变体中,新生叶的数量和花序的形成都会受到影响[12]。
维生素B1能够触发植物的防御系统[13]。当病原体侵染植物时补施维生素B1,植物会大量且迅速地积累致病相关蛋白(pathogenesis related protein,PR)的mRNA,使植物抵抗病原体的能力增强[14]。而且,维生素B1处理会增加水稻对纹枯病及白叶枯病的抗性以及黄瓜对白粉病的抗性[15-16]。
当植物遭受非生物胁迫(例如渗透压、盐和氧化应激胁迫)以及暴露于冷、热和强光条件下,维生素B1含量会增加[17-18],维生素B1生物合成途径关键酶的mRNA转录水平也会增加[19]。对向日葵根部进行外源施加维生素B1,其可溶性糖和K+含量升高、叶片水势含量降低[20]。此外,有研究发现植物对非生物胁迫所诱导损伤的耐受度与维生素B1的含量呈正相关性[21]。
1 维生素B1在植物中的从头生物合成
1.1 维生素B1的分子结构
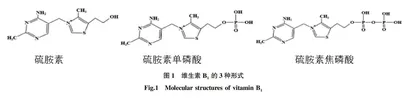
维生素B1主要以硫胺素(thiamin)、硫胺素单磷酸(thiamin monophosphate,TMP)及硫胺素焦磷酸(thiamin pyrophosphate,TPP)3种形式在植物体内存在(图1)。TPP在一些细胞代谢途径中主要起到辅酶的作用。在酸性条件下,硫胺素在嘧啶N1氮和噻唑N3氮上为正电荷;在碱性条件下,随着噻唑环的打开产生硫醇形式[22]。
1.2 维生素B1的生物合成途径
在模式植物拟南芥中,对维生素B1的合成研究比较深入。它主要由噻唑环(4-甲基-5-β-羟乙基噻唑)和嘧啶环(4-氨基-5-羟甲基嘧啶)2个部分组成。2个部分在质体中单独合成,然后结合在一起,最终形成TPP的形式(图2)。
嘧啶是通过嘧啶合成酶(HMP-P synthase,THIC)催化底物5-氨基咪唑核糖核苷酸(5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide,AIR)合成4-氨基-2-甲基-5-羟甲基嘧啶单磷酸(4-amino-2-methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine monophosphate,HMP-P)。在此过程中需要辅助因子还原性酰胺NADH和S-腺苷甲硫氨酸(S-adenosyl methionine,SAM)的参与。最终形成的4-氨基-2-甲基-5-羟甲基嘧啶焦磷酸(4-amino-2-methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine diphosphate,HMP-PP)是由硫胺素磷酸合成酶(thiamine phosphate synthase,TH1)催化HMP-P而完成[22]。
噻唑部分的生物合成是通过噻唑合成酶(HEP-T synthase,THI1)催化底物形成腺苷二磷酸-5-(β-乙基)-4-甲基噻唑-2-羧酸(adenylated thiazole,ADT)。ADT随后在一种迄今为止尚未表征的酶的作用下形成4-氨基-2-甲基-5-羟甲基嘧啶磷酸(4-amino-2-methyl-5-hydroxymethylpyrimidine phosphate,HET-P)。
硫胺素从头合成的2个前体HET-P和HMP-PP被TH1催化,耦联形成TMP。TMP在原核生物中可以直接转化为TPP[23],但在拟南芥中,TMP首先被TMP磷酸酶(TMP phosphatase,TH2)脱磷酸为硫胺素[24-25]。然后被2种硫胺素焦磷酸激酶(thiamine pyrophosphokinase,TPK1和TPK2)焦磷酸化成TPP[26-27]。