喀什地区耕地土壤养分分析及肥力评价
作者: 周荣飞 王海孝
摘要 [目的]明确喀什地区各县市耕地土壤养分丰缺分布状况,并对土壤肥力进行系统性评价分析,为喀什地区耕地土壤养分管理及精准施肥提供科学依据,从而提高喀什地区耕地的可生产能力,促进喀什地区农业产业的可持续发展。[方法]2020—2021 年在喀什地区12 个行政县市区域采集1 030 份耕地土壤样品,分别测定土壤pH、有机质、总氮、碱解氮、有效磷、速效氮、有效铜、有效铁、有效锰、有效锌、有效硼和有效钼含量12 个养分指标,通过运用全国第二次土壤普查养分分级标准及土壤综合肥力指数分析法,对耕地土壤肥力实施了全面、系统的评估分析。[结果]喀什地区耕地土壤 pH 为 7.47 ~ 8.63,土壤pH 偏高,盐碱化现象较为严重;土壤有机质、总氮、碱解氮含量偏低,从各县市区域土壤变异系数来看,土壤中的三者普遍不高,处于中下水平;土壤有效磷和有效钾含量丰富,但土壤变异系数较高,存在分布不均衡现象;耕地土壤中有效铜、有效铁含量在各县市中含量丰富,但仍存在有效铁含量不足的地块;有效锰含量处于中等偏低水平,有效锌和有效硼含量处于中等水平,但土壤样品中的变异系数较高,存在分布不均衡现象;有效钼含量在各县市区域的土壤中含量很低。喀什地区耕地土壤的综合肥力指数为 0.406 9~0.623 4,整体均值为 0.504 0,喀什地区各县市的耕地土壤肥力均处于中等水平,且各县市区域的土壤肥力差异很小。喀什地区各县市的耕地土壤肥力均呈中等水平,土壤pH 含量较高,有机质、总氮和碱解氮含量较低,土壤有效磷、速效钾、有效铁、有效锰、有效锌和有效硼含量存在分布不平衡现象,土壤有效钼含量较低。[结论]各县市应增加有机肥的施入量,进行土壤盐碱化改良,并结合该地的测土施肥结果,开展精准施肥方案,避免造成盲目施肥或者土壤养分不足的现象发生。
关键词 耕地;土壤养分;土壤肥力评价;相关性分析;喀什
中图分类号 X825 文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2024)06-0159-07
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.06.035
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Analysis of Nutrient Content and Fertility Evaluation of Arable Soil in Kashgar Prefecture
ZHOU Rong-fei1,WANG Hai-xiao2
(1.Forest and Fruit Industry Workstation in Kashgar Prefecture,Kashagr,Xinjiang 844000;2.Kashgar Prefecture Agricultural Technology Extension Center kashagr,Kashgar,Xinjiang 844000)
Abstract [Objective]The purpose of this study was to identify the distribution of nutrient abundance and deficiency in the arable land of various counties and cities in Kashgar prefecture,and to conduct a systematic evaluation and analysis of soil fertility,in order to provide scientific basis for the management of arable land soil nutrients and precision fertilization in Kashgar prefecture,thus improving the productive capacity of arable land in the region and promoting the sustainable development of agriculture industry.[Method]Between 2020 and 2021,1 030 samples of cultivated soil were collected from 12 administrative counties and urban areas in Kashgar prefecture,and 12 nutrient indicators such as soil pH,organic matter,total nitrogen,available nitrogen,available phosphorus,available potassium,available copper,available iron,available manganese,available zinc,available boron,and available molybdenum were determined.A comprehensive analysis and evaluation of arable land soil fertility was conducted using the national second soil census nutrient grading standards and soil comprehensive fertility index analysis methods.[Result]The pH range of arable land soil in Kashgar prefecture was 7.47-8.63,with high soil pH values and relatively serious salinization;soil organic matter,total nitrogen,and available nitrogen contents were low,at middle-to-low levels,with lower soil variation coefficients in various counties and urban areas;soil available phosphorus and potassium were abundant,but with higher variation coefficients,indicating imbalanced distribution;available copper and iron concentrations in cultivated soils were rich across counties and cities,though some areas still had insufficient available iron;available manganese levels were medium to low,while available zinc and boron levels were medium,with higher variation coefficients in soil samples,indicating an uneven distribution;available molybdenum levels were very low in the soil of various counties and urban areas.The comprehensive fertility index of arable land soil in Kashgar prefecture ranged from 0.406 9 to 0.623 4,with an overall mean value of 0.504 0,and the soil fertility of arable land in various counties and cities was at a medium level,with little difference among them.The soil fertility of arable land in various counties and cities in Kashgar prefecture was at a medium level,with high soil pH values,low organic matter,total nitrogen,and available nitrogen contents,imbalanced distribution of available phosphorus,available potassium,available iron,available manganese,available zinc,and available boron,and low available molybdenum content.[Conclusion]It is recommended that each county and city increase the application of organic fertilizers,improve soil salinization,and implement precision fertilization plans based on local soil testing results to avoid blind fertilization or insufficient soil nutrient supply.
Key words Arable land;Soil nutrients;Soil fertility evaluation;Correlation analysis;Kashgar
耕地是人与自然共同作用形成的复杂自然有机体[1],耕地的土壤养分含量是植物生长发育的基础,直接决定植物的产量和品质[2],通过土壤肥力评价能够有效摸清耕地土壤质量,有利于耕地资源的修复和高效利用[3]。2022年第三次全国国土调查公布喀什地区耕地面积为99.84万hm2[4],近年来,随着农业生产方式的变革和传统种植结构的变化,加之喀什地区深居内陆,特殊的气候等地理因素也会对耕地造成一定影响,如存在盐渍化、沙化、贫瘠化等一系列耕地质量威胁[5],然而目前针对喀什地区耕地土壤肥力的研究鲜见报道。因此,急需开展喀什地区耕地土壤养分状况分析和肥力评价,以此为依据优化喀什地区耕地管理方式,进而实现喀什地区以耕地为基础的现代化农业可持续发展战略。阿力木江·赛丁等[6]对喀什地区的耕地土壤调查发现有机质、全氮和碱解氮含量处于中下水平,有效磷和速效钾含量处于中等水平。王永旭等[7]对岳普湖县的耕地调查研究发现,全县耕地的特点是土壤养分贫乏、潜在肥力资源不足,表现出明显的干旱区土壤特征。程卫等[8]对英吉沙县的耕地土壤调查发现,存在土质瘠薄、养分缺乏、土壤盐渍化严重等问题。张智斌[9]应用层级分析法发现,喀什地区存在不同程度的低等地,土壤质量较低。
耕地土壤对植物的生长发育至关重要,它是植物吸收养分、水分和氧气的主要来源[10]。前人对喀什地区的耕地土壤研究局限于各县市区域,或者只针对大量元素进行了研究,对喀什地区耕地土壤的养分状况分析及肥力评价缺乏系统性研究。笔者研究了喀什地区耕地土壤养分丰缺和肥力状况,以期为喀什地区耕地的科学施肥和未来现代化可持续管理战略提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
土壤样品采集地主要位于新疆维吾尔自治区喀什地区的12个行政县市区域。喀什地区位于暖温带大陆性干旱气候带[11],现有耕地面积99.84万hm2[4],主要耕地类型以灌淤土、潮土为主[12]。
1.2 样品采集
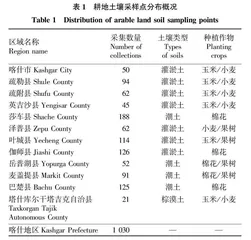
2020—2021年在秋季作物收获后,未进行施肥播种前,采集喀什地区12个行政县市区域的1 030份耕地土壤样品,土壤样品采集分布见表1。采样地选择地势平坦,土壤类型均一,区域种植作物品种、方式一致等具有代表性的地块,每个行政区域的单一采样区域面积约为6.67 hm2,每个采样区域选择“S”形多点取样法[13],按照多点、随机性混合原则,采集一个混合土样,土壤取样深度为0~30 cm,每份保留1 kg样品,装入做好标记的样品袋内,带回实验室风干待测。
1.3 养分测定方法
选用土壤pH等12 个土壤肥力指标作为土壤肥力评价指标,各养分测定标准和方法[14]见表2。
1.4 土壤肥力综合指数计算
1.4.1 土壤单项肥力指标隶属度。
选取12 个指标确定喀什地区土壤肥力评价指标值。常用的隶属度函数有S 型和抛物线型2种[15],其中pH 属于抛物线型隶属函数,其余指标属于S 型隶属函数。
抛物线型隶属函数表达式:
Ai=f(x)=1.0-0.9(x-x3)x4-x3,x3<x<x4
1.0x2≤x≤x3
0.1+0.9(x-x1)x2-x1,x1<x<x2
0.0x≥x4或x≤x1
S型隶属函数表达式:
Ai=f(x)=1.0x≥x2
0.1+0.9(x-x1)x2-x1,x1<x<x2
0.1x≤x1
式中,Ai为评价因子i的隶属值,x为实测值,隶属值为0.1~1.0。依据前人研究结果及全国第二次土壤普查土壤养分分级指标[16-18],确定了各肥力隶属度函数曲线转折点取值(表3)。
1.4.2 土壤肥力单项指标权重系数的确立。根据喀什地区耕地土壤肥力指标间的相关系数,确定权重系数,公式如下:
Wi=NiNi
式中,Ni为养分指标i与其他养分指标间相关系数的平均值,Ni是所有Ni平均值之和。
1.4.3 土壤肥力质量综合指标的确定。
根据单项肥力质量指标隶属度(Fi)和单项肥力质量指标权重(Wi),计算土壤的综合肥力指数(IFI)。公式为:
IFI=ni=1Fi×Wi
式中:n 是参评因子的数量;Fi是第i个因子的隶属度值;Wi是第i个因子的权重。前人研究结果表明[19],隶属度和土壤综合肥力指数取值范围为0~1,指数越接近1,表示土壤的肥力程度越高。结合喀什地区的实际情况确定的综合肥力指数与土壤肥力等级对照见表4。
1.5 数据处理
利用Excel 2021 和Origin 2021 软件统计试验数据并制作图表,应用SPSS 22.0软件计算土壤养分指标之间的相关性,最后基于模糊数学隶属函数模型,对喀什地区土壤肥力进行综合分析评价。
2 结果与分析
2.1 土壤养分统计描述性分析
2.1.1 pH。由表5可知,喀什地区耕地土壤pH分布在7.75~8.40,各县市的土壤pH 变异系数较小,喀什地区耕地土壤呈碱性土壤类型。
2.1.2 有机质含量。
喀什地区耕地土壤有机质含量平均值为13.55 g/kg,属于含量中低水平的耕地,塔什库尔干塔吉克自治县的有机质含量最高,达29.01 g/kg,远高于喀什地区的平均含量,巴楚县的耕地土壤有机质含量最低,仅10.05 g/kg,其余县市的耕地土壤有机质含量的变异幅度较小,主要集中在Ⅳ级和Ⅴ级水平(表5、6)。