河西走廊中部光能资源变化对玉米制种业的影响
作者: 褚超 殷雪莲 万巧锐 狄增文 雷俊
摘要 基于河西走廊中部1981—2020年玉米生长季逐日日照时数以及同期玉米发育期、播种面积和产量资料,采用回归、Mann-Kendall检验和距平法分析玉米生长季光能资源变化特征及其对制种玉米生长发育和制种规模产生的影响。结果表明,1981—2020年河西走廊中部春玉米生长季内光能资源总体呈波动下降趋势。光照强度和光照时间均在前20年随时间呈上升趋势,后20年呈下降趋势。20世纪80年代年太阳总辐射为负距平,90年代为正距平,21世纪以来波动较大,但多以负距平为主。生长季4—6月日照时数呈上升趋势,7—9月呈下降趋势。春玉米播种期略有提前,成熟期推后速率为1.49 d/10 a,全生育期延长。玉米全生育期生长日数与同期日照时数均呈增加趋势,气候倾向率分别为2.87 d/10 a和9.61 h/10 a,两者存在显著正相关。近40年河西走廊中部玉米制种面积和规模明显增加,种植面积递增率为0.23×104 hm2/a,近10年年平均播种面积为8.93×104 hm2,现有规范化玉米制种企业近70家,杂交品种900多个。光能资源等农业气候资源的变化导致河西中部玉米生长发育的变化,从而对制种生产的管理措施和农事活动产生一定影响,在玉米制种过程中尤其要关注气候变化,做到趋利避害,促进河西玉米制种业健康持续发展。
关键词 光能资源;春玉米;生长发育;制种;河西走廊中部
中图分类号 S 162 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2022)01-0220-04
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.01.060
Influence of Radiation Resource Change on Maize Seed Industry in Central Hexi Corridor
CHU Chao1,2,YIN Xue-lian1,WAN Qiao-rui1 et al
(1.Zhangye Meteorological Bureau, Zhangye, Gansu 734000; 2. Zhangye National Climate Observatory, Zhangye, Gansu 734000)
Abstract Based on the daily sunshine hours of maize growing season in central Hexi Corridor from 1981 to 2020 and the data of growth period, planting area and yield in the same period, the variation characteristics of radiation resources in maize growing season and its influence on the maize growth and seed production scale were analyzed by regression, Mann-Kendall test and anomaly method. The results showed that the radiation energy resources showed a fluctuating downward trend during the growing season of spring maize in central Hexi Corridor from 1981 to 2020. The light duration and intensity increased with time in the first 20 years and decreased in the last 20 years. The total solar radiation was negative anomalies in the 1980s and positive anomalies in the 1990s. Since the 21st century, the total solar radiation fluctuated greatly, but most of them were negative anomaly. During the growing season, the sunshine hours increased from April to June, and decreased from July to September. The sowing date of spring maize was slightly advanced, the rate of maturity was 1.49 d/10a, and the whole growth period was prolonged. The growth days and sunshine hours in the whole growth period of maize showed an increasing trend, and the climate tendency rates were 2.87 d/10a and 9.61 h/10a, respectively, and there was a significant positive correlation between the two.In recent 40 years, the area and scale of maize seed production in the central Hexi Corridor increased significantly, and the increasing rate of planting area was 0.23×104 hm2/a, and the average annual planting area in the past 10 years was 8.93×104 hm2. At present, there were nearly 70 standardized maize seed production enterprises and more than 900 hybrid varieties. The change of agricultural climate resources such as radiation energy resources leads to the change of maize growth and development in the central Hexi corridor, which has a certain impact on the management measures and agricultural activities of seed production. In the process of maize seed production, we should pay special attention to the climate change, so as to pursue the advantages and avoid the disadvantages, and promote the healthy and sustainable development of maize seed industry in Hexi Corridor.
Key words Radiation resources;Spring maize;Growth;Seed production;Central Hexi Corridor
基金项目 2020年度甘肃省高等学校产业支撑引导项目(2020C-34);2020年度干旱气象科学研究基金项目(IAM202009);2021年度甘肃省科技计划项目(20JR10RG823)。
作者简介 褚超(1987—),男,山东枣庄人,工程师,从事农业气象以及气候变化方面的研究。
收稿日期 2021-06-01
种业是国家重要的基础性、战略性核心产业,是保障国家粮食安全、提高粮食品质、改善农产品结构的根本要素,也是农业供给侧改革的重要组成部分[1]。近年来,玉米制种业已成为河西中部地区重要的支柱产业,也是一大特色产业,种植历史已有300多年,目前种植面积达近百万亩,生产能力达到满足全国玉米制种市场50%的要求,每年提供的玉米种子占整个市场份额的40%,因此也是现在全国最大的玉米制种基地,已成为我国制种玉米四大主产区之一。
气候资源对玉米生长有着重要的影响,适宜的气候资源有利于制种玉米优质高产,其中光能资源是重要的影响因素。光能是农作物生长发育和产量、品质形成的能量源泉,在植物体内干物质中,有90%左右是直接或间接地来自光合作用的产物。目前有关光能资源的研究多集中在多时空尺度的年季光能资源变化[2-9]、玉米生育期内光热水条件变化[10-19]等方面,而针对光能资源对制种玉米生产影响的研究尚不多见。笔者利用河西走廊中部1981—2020年玉米生育期逐日日照时数以及同期玉米发育期、产量资料,从光照强度和光照时间2个方面分析制种玉米生长季光能资源变化特征及其对玉米制种业产生的影响,认识玉米生产中的主要光能资源问题,对指导制种玉米生产、防灾减灾有重要的现实意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料选取
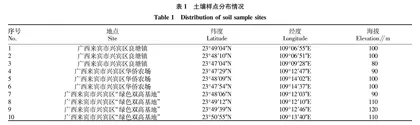
选用河西中部(张掖市)1981—2020年玉米播种面积、产量和生长季(4—9月)逐日日照时数资料,以及1984—2020年玉米生育期资料,玉米为制种玉米,春性,中早熟,观测对象为母本,抽雄开花期为父本。气象数据选取距离玉米观测点较近的气象站。气象和玉米生育期资料来源于张掖市气象局,为实际观测值。玉米播种面积和产量资料来自张掖市统计局。
1.2 研究方法
将玉米生育期划分为出苗—拔节期(营养生长期)、拔节—吐丝期(营养生长与生殖生长并进期,简称并进期)、吐丝—成熟期(生殖生长期)3个阶段。
①采用目前应用比较广泛的基于日照观测指标的太阳总辐射气候学方法[20],计算公式为Q=Q0(a+bS),式中,Q表示月太阳总辐射(MJ/m2);Q0是月天文总辐射值(MJ/m2);S是日照百分率(%);a和b为经验系数。
②采用一元线性回归、距平法和Mann-Kendall检验[21]分析光能资源变化趋势,即xt=a0+a1t,t=1,2,…,n,式中,xt为气象要素的拟合值;a1×10称为气候倾向率,表示气象要素每10年的变化率。
③对春玉米产量采用正交多项式拟合趋势方程的方法,分离出趋势产量(Yt)和气象产量(Yw)。
④用回归分析求取春玉米关键生长阶段太阳总辐射、日照时数与生长日数和气象产量的回归系数,分析光能资源在各个生育期对春玉米生长的影响情况。
2 光能资源变化分析
2.1 太阳总辐射
从图1a可以看出,近40年来张掖市春玉米生长季太阳总辐射总体呈下降趋势,且具有明显的波动性,但下降趋势不明显,气候倾向率仅为-3.98 MJ/(m2·10 a);太阳总辐射最少的年份为2010年,仅为3 687.20 MJ/m2,最多的年份为1990年,为4 059.87 MJ/m2,最多年比最少年多10.11%。1981—1990、1991—2000、2001—2010和2011—2020年春玉米生长季太阳总辐射拟合方程分别为y=23.672x+3 684.8、y=4.868x+3 901.1、y=-17.938x+3 933.9、y=-12.251x+3 900,各年代年平均太阳总辐射分别为3 814.96、3 927.90、3 835.20、3 832.62 MJ/m2。从Mann-Kendall检验结果看,1981—2020年张掖市春玉米生长季太阳总辐射没有出现显著的突变现象。可见,张掖市玉米生长季太阳总辐射变化1981—1990年上升较为明显,1991—2000年呈波动性上升,趋势不明显,后20年呈显著下降趋势。张掖市春玉米生长季太阳总辐射距平变化呈现较为明显的年代特征(图1 b),20世纪80年代为负距平,90年代为正距平,21世纪以来波动较大,但多以负距平为主。
2.2 日照时数
近40年来张掖市春玉米生长季日照时数随时间变化具有一定的波动性,线性拟合方程为y=-0.087 6x+1 675.9(图2);
1981—1990、1991—2000、2001—2010和2011—2020年春玉米生长季日照时数拟合方程分别为y=16.508x+1 555.6、y=3.753x+1 706.6、y=-12.932x+1 726.1、y=-7.688x+1 709.9。由此可见,近40年来张掖市春玉米生长季日照时数总体为下降趋势,但前20年随时间呈上升趋势,后20年呈下降趋势。从生长季内各月日照时数来看,4、5、6月日照时数呈上升趋势,气候倾向率分别为7.00、1.16、1.01 h/10 a;7月为下降趋势,但幅度较小,气候倾向率仅为-0.10 h/10 a;8、9月为下降趋势,气候倾向率分别为-4.91、-5.04 h/10 a。