基于数据挖掘及网络药理学方法探讨中药复方抗上呼吸道感染的用药规律及作用机制
作者: 何海 张小荣 赵沙沙 邵晶
摘要 [目的]研究中药复方治疗上呼吸道感染的用药规律及核心中药的作用机制。[方法]通过CNKI数据库收集临床用于上呼吸道感染的中药复方,采用Excel 2010及SPSS 24.0 软件对纳入标准的中药进行频次、性味归经、四气五味及功效统计,并对频数大于40的中药进行聚类分析;使用中药系统药理学分析平台数据库(TCMSP)对频数较高且在聚类分析中聚为一类的配伍中药进行成分、靶点筛选,将其靶点与在 GeneCards 数据库和Malacards数据库中筛选得到的上呼吸道感染的疾病靶点进行匹配,获取高频中药治疗上呼吸道感染的关键靶点;采用STRING 平台对关键靶点进行蛋白相互作用(PPI)网络分析;采用DAVID 数据库对关键靶点进行京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)通路富集分析;通过Cytoscape 3.6.1软件构建“中药-活性成分-关键靶点-通路”网络,并进行拓扑分析。[结果]共获得符合标准的中药复方464首,涉及中药414味;其中以补虚药、清热药较多见,归肺、胃经居多,以寒温、苦辛为主;累计频次最高且聚为一类的是黄芪、防风、白术。获得活性成分共32个,核心成分包括槲皮素、山柰酚、异鼠李素、汉黄芩素、β-谷甾醇、5-O-甲维阿斯米醇、防风色原酮等;关键靶点175个,核心靶点包括AKT1、MAPK1、TNF、RELA、JUN、TP53、IL6等;通路137条,主要通路包括癌症通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、TNF信号通路、Toll样受体通路等。[结论]治疗上呼吸道感染的中药复方中以补虚药多见,常配伍清热药、止咳化痰平喘药、消食药等。组方中以黄芪、防风、白术配伍频次最高,其作用机制可能是通过槲皮素、山柰酚、异鼠李素、汉黄芩素、β-谷甾醇、5-O-甲维阿斯米醇、防风色原酮等活性成分,作用于AKT1、MAPK1、TNF等关键靶点,及PI3K-Akt信号通路、TNF信号通路、Toll样受体通路等,共同发挥治疗作用。
关键词 上呼吸道感染;中药复方;数据挖掘;网络药理学;用药规律;作用机制
中图分类号 R 285 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2022)03-0178-08
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.03.048
Exploring the Rule of Medication and Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine Compound Prescription Against Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Based on Data Mining and Network Pharmacology Methods
HE Hai,ZHANG Xiao-rong,ZHAO Sha-sha et al
(Gansu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Lanzhou,Gansu 730000)
Abstract [Objective]To explore the medication rule of traditional Chinese medicine compound against upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) and the mechanism of action of core traditional Chinese medicine (TCM).[Method]All compounds of clinical research treating upper respiratory tract infection were collected from CNKI database. Excel 2010 and SPSS 24.0 software were used to make statistics of the frequency, nature, taste, meridian tropism, four properties and five flavors and their efficacy of the TCM, and systematic cluster analysis was carried out on the Chinese medicines with frequency more than 40 times. The TCM with higher frequencies and being clustered together were searched for their components and targets through the TCMSP database, and those matched with the disease targets of URTI screened in GeneCards database and Malacards database, so as to obtain the key targets of high-frequency TCM against URTI. The key targets were then used to construct and analyze PPI network and KEGG pathway with STRING and DAVID database. “The network of traditional Chinese medicine-active ingredient-key target-pathway” was constructed by Cytoscape 3.6.1 software, and the topology analysis was carried out. [Result]A total of 464 Chinese herbal compounds were obtained, involving 414 Chinese herbal medicines. Among them, TCM that restoring deficiency and heat-clearing drug, with lung and stomach tropism, cold, warm and bitter and pungent in flavor, were shown the most common;The Astragali radix, radix sileris and Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz were the most frequently used and being clustered together. A total of 32 active components were obtained, and the core components included quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, wogonin, β-sitosterol, 5-O-Methylvisamminol, divaricatol and so on. There are 175 key targets against URTI, and the core targets include AKT1, MAPK1, TNF, RELA, JUN, TP53, IL6, etc. There are 137 pathways involved, including cancer pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, toll-like receptor pathway and so on. [Conclusion]Commonly used TCM for the traditional Chinese medicine compound were those restore deficiency, and they are often combined with heat-clearing drugs, drug for relieving cough, phlegm and asthma, and digestant drugs. The compatibility of the astragali radix, radix sileris and Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz is the most common compound, it may be mainly through quercetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, wogonin, β-sitosterol, 5-O-Methylvisamminol, divaricatol and other active ingredients to act on key targets such as AKT1, MAPK1, TNF, and PI3K-Akt signal pathway, TNF signal pathway and Toll-like receptor and other signaling pathways,to take effects together.
Key words Upper respiratory tract infection;Traditional Chinese medicine compound prescription;Data mining;Network pharmacology;Rule of medication;Mechanism of action
基金项目 兰州市城关区科技计划项目(2020-2-2-2);甘肃省中药制药工艺工程研究中心开放课题(ZYGY202004);甘肃中医药大学科学研究与创新基金项目(2020KCZD-2);中医药公共卫生服务补助专项子课题(2305191901)。
作者简介 何海(1997—),男,甘肃山丹人,硕士研究生,研究方向:中药药效物质基础及质量控制。
通信作者,教授,博士,硕士生导师,从事中药药效物质基础及质量控制研究。
收稿日期 2021-04-19
呼吸道感染是当前世界导致人类死亡的主要原因之一,全世界有超过10亿人受到影响[1-2]。其中,上呼吸道感染(upper respiratory tract infection,URTI)是由细菌、病毒、自身免疫缺陷等因素诱发[3-4],在临床上发病率较高,且治疗控制不及时就容易使炎症深入蔓延,鼻炎、咽炎、喉炎、扁桃体炎等都属于上呼吸道感染的类型[5]。临床常用抗生素作为治疗上呼吸道感染的首选药物,但由于使用抗生素产生的不良反应、耐药性以及滥用抗生素导致的问题,补充和替代疗法在预防和治疗上呼吸道感染中成为研究热点[6]。中医是一种基于临床实践的经验性医学,从中医角度来说,上呼吸道感染属于感冒的范畴,病因多为“正虚邪恋”[7],许多相关的基础试验和临床用药都表明中医药在治疗上呼吸道感染方面具有优势。为了更好地继承众医家的用药经验,该研究借助数据挖掘与网络药理学分析方法,对治疗上呼吸道感染的中药复方进行整理分析,挖掘中药治疗上呼吸道感染的用药规律,并探索高频中药的可能作用机制,从而为提高中医药治疗上呼吸道感染的有效性和科学性提供依据。
1 资料与方法
1.1 数据来源
通过中国知网(https://www.cnki.net/),将“上呼吸道感染”和“中医药”作为主题词,检索有关中医药治疗上呼吸道感染的相关文献(1991年10月—2020年12月)。获得文献626篇,内含相关组方700余首。
1.2 处方纳入标准
明确被诊断为上呼吸道感染的患者用药处方,组方完整、疗效确切且以口服入药为主要用药手段的处方。
1.3 处方排除标准
联合用药或用于动物和细胞试验的处方,交叉重叠的处方,只录入一篇。
1.4 数据处理
共筛选得到相关组方464首,将所有组方涉及的中药按全国中医药行业高等教育“十三五”规划教材《临床中药学》及2020年版《中华人民共和国药典》中所述,对其名称、性味归经、功效进行规范化处理,如将“仙灵脾”规范为“淫羊藿”,将“恶实”规范为“牛蒡子”,将“羚羊角粉”规范为“羚羊角”等,并将处理过的数据录入Excel表格中,整个录入过程由双人核对完成。
1.5 数据分析
利用Excel对已录入的中药及其性味归经、功效等分别进行频数统计。运用Excel对上述中药信息进行处理,并以矩阵的形式导入SPSS 24.0软件中进行聚类分析,根据分析结果制作相关图表。然后通过中药系统药理学分析平台数据库(TCMSP,http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmspsearch.php)、Malacards数据库(https://www.malacards.org/)、 GeneCards 数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)等对聚类分析后所得的频数较高且聚为一类的共性较大的中药进行成分和靶点的筛选。将筛选得到的靶点与上呼吸道感染的疾病靶点相匹配,获取高频中药作用于上呼吸道感染的关键靶点。通过STRING 平台(https://string-db.org/)和京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)对关键靶点进行蛋白相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络分析和通路富集分析。最后,通过Cytoscape 3.6.1软件构建“中药-活性成分-关键靶点-通路”网络图,并进行拓扑分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1 用药频次统计
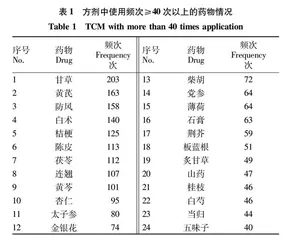
对筛选得到的464首处方进行用药统计,共涉及中药414味,累计应用频次4 439次。其中,使用频次≥40次的中药共有24味,使用频次最多的是甘草,共计203次。排名靠前的中药包括甘草、黄芪、防风、白术、桔梗等。详见表1。
2.2 性味归经统计
经统计(表2),414味中药的属性中,性寒的药物最多,占37.44%;五味属苦的药物最多,占46.86%;归肺经的药物最多,占53.14%。
2.3 主要功效统计
根据2020版《中华人民共和国药典》和《临床中药学》教材,对414味中药进行主要功效分类统计。结果发现(表3),使用频次较高的是清热药和补虚药,均占19.08%,解表药和止咳平喘药次之,各占10.39%和8.70%。补虚药中又以补气药居多,占44.30%。
2.4 高频中药系统聚类分析
运用 SPSS 24.0 软件对频次≥40次的中药进行系统聚类分析,共分为6类,如图1所示。黄芪、防风、白术聚为一类且出现次数最高。
2.5 高频药组抗上呼吸道感染作用机制研究
2.5.1 成分及靶点筛选。