耐低温降解纤维素菌株的筛选及复合菌系构建
作者: 路垚 刘雅辉 孙建平 何宗均 赵琳娜 戴相林 赵子婧
摘要 [目的]筛选适合我国北方冬春季秸秆降解的高效低温纤维素降解菌株。[方法]在低温地区采集土壤,10 ℃初筛耐低温菌株,通过刚果红染色液法进行复筛,利用DNS法测定CMC酶活性。将筛得菌株和实验室自存菌株结合拮抗试验构建复合菌系,测定复合菌系CMC酶活性,测定秸秆降解率,并对代表性菌株进行产酶条件优化,对最终确定的复合菌系中的菌株进行分子生物学鉴定。[结果]10 ℃低温培养初筛得到55株耐低温菌株,刚果红染色法复筛得到8株具有明显水解圈的单菌株,其中包括细菌3株、真菌2株、放线菌3株,其中纤维素酶活性最高达到47.0 U/mL;根据拮抗试验构建了2个复合菌系,其纤维素酶活性分别达到31.0和53.0 U/mL;秸秆降解试验中,实验室和沙袋法的复合菌系2对秸秆的降解率分别达31.8%和45.1%,显著高于复合菌系1和对照组;对JGDZTX3进行产酶条件优化,确定最佳氮源为牛肉膏,培养温度为10 ℃,培养时间为4 d,初始pH为7,在此条件下CMC酶活性达到66.5 U/mL,这4个条件对产酶均有显著影响(P<0.05);对复合菌系2的4个未知菌株进行鉴定,鉴定结果分别为白蚁菌、葡萄球菌、长柄木霉、芬莱氏链霉菌。[结论]通过该试验筛选得到的耐低温可降解纤维素复合菌系有较强的纤维素分解能力,在北方低温地区有良好的应用前景。
关键词 纤维素降解菌;复合菌系;低温;纤维素酶;筛选;菌株鉴定
中图分类号 S182 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2022)10-0006-05
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2022.10.002
Screening of Low Temperature Cellulose Degradation Strains and Construction of Complex Microbial System
LU Yao1,LIU Ya-hui2,SUN Jian-ping2 et al
(1.Institute of Agricultural Resources and Environment Sciences,Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Tianjin 300384;2.Institute of Coastal Agriculture, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences,Tangshan,Hebei 063299)
Abstract [Objective] In order to screen the high efficiency low temperature cellulose degradation strains suitable for winter and spring straw degradation in north China. [Method]Soil samples were collected in low temperature area, low temperature strains were screened at 10 ℃, the isolated strains were screened by Congo red staining solution, and CMC enzyme activity was determined by DNS method. The complex microbial system was constructed by combining the screened strain and the laboratory self-existing strain with antagonistic test. CMC enzyme activity of the complex microbial system was determined, and the straw degradation rate was determined. The enzyme production conditions of the representative strain was optimized, and the strains in the final determined complex microbial system were identified by molecular biology. [Result]A total of 55 low temperature strains were obtained by initial screening at 10 ℃, and 8 strains were obtained by Congo red staining after screening, including 3 strains of bacteria, 2 strains of fungi and 3 strains of actinomycetes with obvious hydrolytic circles. The highest cellulase activity reached 47.0 U/mL. According to the antagonistic test, the cellulase activity of two complex microbial systems reached 31.0 and 53.0 U/mL, respectively. In the straw degradation test, the degradation rates of the compound strain 2 in the laboratory and the sandbag method were 31.8% and 45.1%, respectively, which were significantly higher than those of the compound strain 1 and the control group.The optimum conditions for JGDZTX3 enzyme production were optimized, and the optimal nitrogen source was beef paste, culture temperature was 10 ℃, culture time was 4 d, and initial pH was 7. Under the optimum conditions, CMC enzyme activity reached 66.5 U/mL ,all the four conditions had significant effects on enzyme production (P< 0.05).The four unknown strains of the complex microbial system were identified, and the identification results were Isoptericola sp., Staphylococcus sp., Trichoderma longibrachiatum and Streptomyces finlayi.[Conclusion]The low temperature cellulose-degradable complex microbial system screened by this experiment has strong cellulose-decomposing ability, and has a good application prospect in the low temperature area of north China.
Key words Cellulose degradation strains;Complex microbial system;Low temperature;Cellulase;Screening;Strain identification
基金项目 河北省省级科技计划项目(19227307D);天津市农业科技成果转化与推广项目(201701090)。
作者简介 路垚(1989—),女,山东临沂人,助理研究员,硕士,从事农业微生物研究。通信作者,副研究员,从事农业微生物研究。
收稿日期 2021-12-06;修回日期 2022-01-18
我国有大量秸秆,每年各类秸秆产生量高达8 亿t,如果能合理利用,将会是很重要的生物资源[1-2]。秸秆的资源化处理有多种方式,其中微生物降解的方法具有安全性高、能耗低等优点被广泛应用[3]。但是自然条件下土壤中纤维素分解菌的数量较少,降解效率低,秸秆直接还田后不能被快速分解,因此通常人工添加一些纤维素分解菌加快秸秆的腐解[4-5]。已发现的纤维素分解菌有很多种,涵盖了细菌、真菌、放线菌等各类菌株[6],国内外也有很多人在自然界中进行了纤维素分解菌菌株的筛选和应用。
郑丽等[7]在木薯生境里分离筛选得到57株纤维素分解菌株;姜立春等[8]从绵阳湿地朽木和土样中,筛选得到28株产纤维素酶的细菌菌株;赵旭等[9]在土壤中筛选的Penicillium sp.D5菌株,以玉米秸秆为碳源发酵10 d,可使玉米秸秆减重29.8%;Selvam等[10]研究表明纤维素降解是菌株间相互协同作用产生的结果;王天生等[11]研究发现复合菌系的纤维素分解能力好于单一菌株;王垚等[12]研究表明 H57.1 和 H08.1菌株复合后具有较高的秸秆分解能力,其秸秆降解率可达到55.7%。
微生物降解受环境影响较大,很多纤维素分解菌在低温环境下不能生长代谢,不能正常发挥降解作用。我国北方地区冬春季温度低,常温条件下筛选的纤维素分解菌难以发挥作用。目前,对纤维素分解菌的研究主要集中在常温环境的筛选,对低温环境下纤维素分解菌的研究相对较少[13-14]。该研究通过从河北滨海区低温土壤中分离筛选纤维素酶活性较高的菌株,构建复合菌系,以期为北方低温地区秸秆的资源化利用提供菌种资源。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品和培养基
1.1.1 样品来源。
河北省唐山市曹妃甸区河北省农林科学院研究基地土样,分别为水稻田秸秆还田2年土、水稻田秸秆还田3年土、水稻秸秆还田咸水土、秸秆堆置土。存放于自封袋中,封口,于4 ℃保存备用。
1.1.2 培养基。
(1)CMC分离培养基。CMC-Na 10 g,(NH4)2SO4 4 g,K2HPO4 1 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,KH2PO4 1 g,蛋白胨1 g,酵母膏1 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.0~7.2。
(2)种子培养基。(NH4)2SO4 3.0 g,KH2PO4 1.0 g,FeSO4·7H2O 5.0 mg,MnSO4·H2O 1.6 mg,CaCl2 0.1 g,ZnSO4·7H2O 1.7 mg,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,CoCl2 2.0 mg,NaCl 0.1 g,葡萄糖 20 g,蛋白胨5 g,酵母膏1 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.0~7.2。
(3)牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基。牛肉膏5 g,蛋白胨10 g,NaCl 5 g,琼脂15~20 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.0~7.2。
(4)PDA培养基。马铃薯200 g,葡萄糖20 g,琼脂15~20 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH自然。
(5)高氏一号培养基。可溶性淀粉20 g,KNO3 1 g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g,K2HPO4 0.5 g,FeSO4·7H2O 0.01 g,NaCl 0.5 g,琼脂 20 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.4~7.6。
(6)秸秆降解培养基。秸秆3 g,CMC-Na 10 g,(NH4)2SO4 4 g,K2HPO4 1 g,MgSO4· 7H2O 0.5 g,KH2PO4 1 g,蛋白胨1 g,酵母膏1 g,H2O 1 000 mL,pH 7.0~7.2。
1.2 菌株分离筛选
1.2.1 菌株的初筛。
将采集到的土壤样品用无菌水制成10-4、10-5、10-6稀释度的菌悬液,在CMC培养基上涂布,放置生化培养箱10 ℃培养5 d。将初筛得到的菌株在固体平板上分别编号,并分别划线纯化,然后每个平板倒入15 mL刚果红溶液(1 mL/mg)染色30 min,用1 mol/L氯化钠溶液脱色2~3次,只保留有透明圈的对应标号菌株,将得到的细菌保存至牛肉膏蛋白胨试管斜面培养基,真菌保存至 PDA 试管斜面培养基,放线菌存放至高氏一号试管斜面培养基,放置 4 ℃冰箱保存。
1.2.2 菌株的复筛。
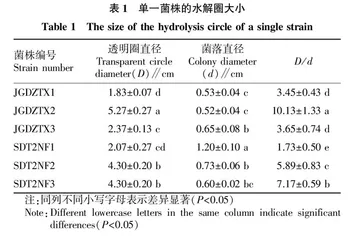
将保存的菌株接种于CMC培养基,放至摇床10 ℃恒温振荡培养5 d,在CMC固体平板上放置牛津杯,在牛津杯中加入100 μL菌液,10 ℃恒温培养箱培养5 d,取出牛津杯,测量菌落直径(d),每个平板倒入15 mL 刚果红溶液(1 mL/mg)染色30 min,然后用 1 mol/L氯化钠溶液清洗脱色 2~3次,测量透明圈的直径(D),每个菌株做3个重复。
1.3 DNS法测定酶活
1.3.1 原样酶液的制备。
将待测菌株接种到种子培养基,10 ℃恒温振荡培养3 d,转接至CMC分离培养基培养5 d,取菌液10 mL,3 000 r/min离心10 min,离心后的上清液即为原样酶液,供测试用。