流动注射分析仪法检测生活饮用水中氨的方法建立及应用
作者: 卢义柱 邓超 盛晓宇
摘 要:目的:建立流动注射分析仪测定生活饮用水中氨的方法,以替代《生活饮用水标准检验方法 无机非金属指标》(GB/T 5750.5—2006)中的纳氏试剂分光光度法。方法:样品和试剂通过流动注射分析仪被带入到连续流动的载流液中。基于NH4+离子、水杨酸钠、氯在碱性条件下反应生成显色复合物,以硝普钠(亚基铁氰化钠)为催化剂,在660 nm波长下比色测量。氨标准样品和23份实际水样用纳氏试剂分光光度法检测,与流动注射分析仪法进行对比分析。结果:氨的浓度在0~2.00 mg·L-1,流动注射分析仪法的线性相关系数为
0.999 9;对氨浓度为0.018 mg·L-1的样品进行15次测定,计算得出方法检出限为0.001 4 mg·L-1;对两种不同浓度的实际水样进行加标回收试验,加标回收率为96.8%~101.7%;对标准样品的实际检测结果在允许误差范围内,精密度优于纳氏试剂分光光度法;经统计分析,流动注射分析仪法标准偏差为0.003 9 mg·L-1,低于纳氏试剂分光光度法的(0.024 4 mg·L-1),t=8.323,P=0.00<0.05,两种检测方法的差异有统计学意义;对23份农村生活饮用水分别用流动注射分析仪和纳氏试剂分光光度法进行测定,比较两种方法的测定结果,t=1.680,
P>0.05,两种检测方法结果的差异无显著性。结论:相比于纳氏试剂分光光度法,流动注射分析仪法具有方便、快捷、高效和低消耗等特点,其准确性和自动化程度优于国家标准方法,适用于生活饮用水中的氨指标的检测。
关键词:流动注射分析仪法;纳氏试剂分光光度法;生活饮用水;氨
Establishment and Application of Flow Injection Analyzer Method for Determination of Ammonia in Drinking Water
LU Yizhu, DENG Chao, SHENG Xiaoyu
(Shucheng County Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shucheng 231300, China)
Abstract: Objective: To establish a method for the determination of ammonia in drinking water by flow injection analyzer to replace the spectrophotometric method of Nessler’s reagent in the GB/T 5750.5—2006. Method: The samples and reagents were brought into the continuous flow carrier liquid by the flow injection analyzer. According to the reaction of NH4+, sodium salicylate and chloro-alkaline conditions, color development complex was formed. Sodium nitroprusside (sodium ferricyanide) was used as catalyst, and colorimetric measurements were made at 660 nm wavelength. Ammonia standard samples and 23 actual water samples were detected by spectrophotometry with Nessler’s reagent and compared with flow injection analyzer. Result: When the concentration of ammonia was 0~2.00 mg·L-1,
the linear correlation coefficient of flow injection analyzer was 0.999 9. The sample with ammonia concentration of 0.018 mg·L-1 was determined for 15 times, and the detection limit of the method was calculated to be 0.001 4 mg·L-1. Two kinds of water samples with different concentrations were recovered by adding standard, and the recovery rate was 96.8%~101.7%. The accuracy of the actual test results of the standard samples is better than that of the Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry within the allowable error range. After statistical analysis, the standard deviation of the flow injection analyzer method was 0.003 9 mg·L-1, which was lower than 0.024 4 mg·L-1 of the Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry method, t=8.323, P=0.00<0.05, and the difference between the two detection methods was statistically significant. 23 samples of rural drinking water were determined by flow injection analyzer and Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry. The results of the two methods were compared, t=1.680, P>0.05, and there was no significant difference between the two methods. Conclusion: Compared with the Nessler’s reagent spectrophotometry, the flow injection analyzer method has the characteristics of convenience, fast, high efficient and low consumption, its accuracy and automation is better than the national standard method, which is suitable for the detection of ammonia index in drinking water.
Keywords: flow injection analyzer method; Nesser’s reagent spectrophotometry; drinking water for domestic use; ammonia
氨含量是判断生活饮用水是否合格的一项重要技术指标,氨的浓度能够反映该饮用水是否被有机物污染,且氨能在配水系统中减弱消毒剂的消毒效果,生成亚硝酸盐[1]。如果长期饮用氨含量高的水,水中的亚硝酸盐将和蛋白质结合形成亚硝胺,这是一种强致癌物质,对人体健康极为不利[2-3]。
目前,测定氨常用的方法有纳氏试剂分光光度法、水杨酸盐分光光度法、酚盐分光光度法等,虽然传统的分光光度法运用相对普遍,且具有操作简单、灵敏度高等优点,但是随着生活饮用水检测技术的不断发展,传统化学分析法已无法满足日常检测工作的需求[4-5]。连续流动注射分析法采用气片段连续流动分析技术自动分析样品,具有自动化程度高、分析过程简便、快速等特点。生活饮用水中氨项目的检测,舒城县疾病预防控制中心之前采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,试验过程中要用到有毒物质碘化汞。为了更好地保护环境和实验室人员的身体健康,笔者用Futura2流动注射分析仪测定生活饮用水中的氨,对该方法的准确度、检出限、精密度和加标回收率等重要参数进行测定,用Futura2流动注射分析仪测定购买的标准样品及23份生活饮用水实际水样,并与生活饮用水标准检验方法中的纳氏试剂分光光度法进行了对比分析。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料与试剂
氨标准液,GBW(E)080220(定值日期:2020年11月16日,效期:2022年11月15日);氨标准样品,GSB 07-3164-2014(生态环境部标准样品研究所,定值日期:2019年12月,有效期限:2024年11月,标样批号:2005137);水杨酸钠、亚硝基铁氰化钠、二氯异腈脲酸钠、氯化钾和氢氧化钠,均为分析纯。
1.2 仪器与设备
流动注射分析仪,Futura2,法国AMS公司;可见光分光光度计,T6,北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 流动注射分析仪法标准曲线绘制
分别吸取10 μg·mL-1氨标准使用液0 mL、
0.10 mL、0.20 mL、0.30 mL、0.50 mL、1.00 mL和
2.00 mL于10 mL的PE管中,加水定容至刻度线,得到系列浓度分别为0 mg·L-1、0.10 mg·L-1、
0.20 mg·L-1、0.30 mg·L-1、0.50 mg·L-1、1.00 mg·L-1和
2.00 mg·L-1,用Futura2流动注射分析仪检测。
1.3.2 纳氏试剂法标准曲线绘制
分别吸取10 μg·mL-1氨标准使用液0 mL、
1.00 mL、2.00 mL、4.00 mL、6.00 mL、8.00 mL和10.00 mL于50 mL玻璃比色管中,加水定容至刻度线,得到系列浓度分别为0 mg·L-1、0.20 mg·L-1、
0.40 mg·L-1、0.80 mg·L-1、1.20 mg·L-1、1.60 mg·L-1和
2.00 mg·L-1,分别加1 mL酒石酸钾钠溶液,再加入
1.00 mL纳氏试剂,以去离子水为参比,在420 nm波长、1 cm光径条件下,测定吸光度对氨浓度进行线性回归。
1.3.3 有证标准样品的测定
取10 mL购买的氨标准样品(GSB 07-3164-2014),
定容至500 mL容量瓶中,最终使用浓度为1.445 mg·L-1,分别用流动注射分析仪法和纳氏试剂分光光度法进行测
定。流动注射分析仪法取最终使用浓度为1.445 mg·L-1的氮标准样品,按1.3.1方法测定10份样品,根据标准曲线确定其浓度;纳氏试剂分光光度法取最终使用浓度为1.445 mg·L-1的氮标准样品,按上述1.3.2方法测定10份样品,根据标准曲线确定其浓度。
1.3.4 统计方法
用IBM SPSS Statistics 26软件进行统计学分析,采用t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果与分析
2.1 标准曲线绘制
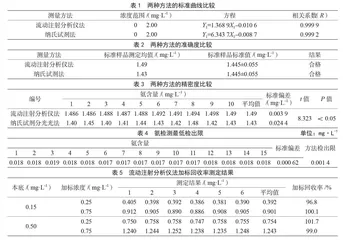
以系列浓度(X)为横坐标,以吸光度(Y)为纵坐标,分别绘制两种方法的标准曲线方程,详见表1。
2.2 两种方法的准确度比较
分别用流动注射分析法和纳氏试剂法两种方法检测购买的标准样品,检测的结果值与标准样品证书上所标示值进行比较,两种方法的检测结果均在标准值的误差范围之内,结果见表2。
2.3 方法精密度
分别用两种方法检测购买的标准样品,通过统计学处理,求得两者的精密度。经过统计处理,流动注射分析仪法标准偏差(0.003 9 mg·L-1)低于纳氏试剂法(0.024 4 mg·L-1),t=8.323,P=0.00<0.05,两种检测方法精密度差异有统计学意义,流动注射分析仪法精密度优于纳氏试剂法,结果见表3。
2.4 最低检出限
选用氨含量与空白浓度接近的0.018 mg·L-1的样品进行15次重复测定,按公式(检出限=K×SD/S,K常取3)计算流动注射分析法的检出限,得出本次试验的标准偏差为0.000 62 mg·L-1,最低检出限为
0.001 4 mg·L-1,结果见表4。
2.5 加标回收试验
本底浓度为0.15 mg·L-1、0.50 mg·L-1的样品溶液中,加标浓度分别为0.25 mg·L-1和0.75 mg·L-1,对加标后的样品分别连续测定6次,加标回收率在96.8%~101.7%,其测定结果及加标回收率见表5。