植物纤维对MS培养液中烟酸和维生素B<sub>6</sub>的水平浸润传质效应
作者: 周春长 杜亚填 彭凤珍
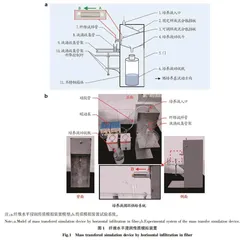
摘要 为筛选用于所发明帘状锚固培养生物反应器培养床的纤维,模拟反应器通过纤维丝将培养液浸润传质到愈伤组织细胞的流程创制了“纤维水平浸润传质模拟装置”,结合改进的烟酸、维生素B6、维生素B1 HPLC 同步检测法,流动相洗脱体系采用庚烷磺酸钠溶液∶乙腈=90∶10(V∶V)等度洗脱等,研究16种纤维集束对MS培养液中烟酸、维生素B6和维生素B1的水平浸润传质效应。结果表明,16种纤维集束水平浸润传质具有升降MS培养液中烟酸、维生素B6浓度的效应,但效应持续时间均不超过84 min,且具有较明显种类间差异,秸秆和木材纤维的作用效应弱于茎皮和竹材纤维。慈竹、青皮竹竹材纤维集束中烟酸浓度的升降较明显,在0.02~2.58 μg/mL,苎麻茎皮纤维集束中烟酸浓度的升幅最高,达3.17 μg/mL,是原浓度的5倍多,持续时间72 min。青皮竹、毛竹竹材纤维集束传质液中维生素B6的浓度出现下降至零点的效应,苎麻茎皮纤维集束中出现较原浓度升高2倍的高点,其他种类纤维集束中3种维生素的浓度升降较小。虽然植物纤维集束会导致传质液中3种维生素的浓度升高或降低,但作用效应的持续时间均只在纤维集束饱和吸液后的84 min内。
关键词 植物纤维;MS培养液;烟酸;维生素B6;浸润传质效应;HPLC
中图分类号 Q 813.1+1 文献标识码 A
文章编号 0517-6611(2024)16-0006-07
doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2024.16.002
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Horizontal Infiltration and Mass Transfer Effects of Plant Fibers on Nicotinic Acid and Vitamin B6 in MS Culture Medium
ZHOU Chun-chang,DU Ya-tian,PENG Feng-zhen
(Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Forest Products and Chemical Engineering,Jishou University,Zhangjiajie,Hunan 427000)
Abstract In order to screen the fibers used in Curtain-liking Anchoring Culture Bioreactor,a “Fiber Horizontal Infiltration Mass Transfer Simulation Device” was created by simulating the process of the reactor to infiltrate and transfer the culture solution to the callus cells through the fiber silk.In combination with the improved simultaneous detection methods for nicotinic acid,vitamin B6,and vitamin B1 HPLC,the mobile phase elution system used sodium heptanesulfonate solution:acetonitrile=90∶10(V∶V) equal degree elution,etc.The effects of mass transfered by horizontal infiltration in 16 plant fiber bundles on nicotinic acid,vitamin B6 and vitamin B1 of MS medium were studied.The results showed that the horizontal infiltration mass transfer in 16 plant fiber bundles had the effect of increasing or decreasing the concentration of nicotinic acid and vitamin B6 of MS culture medium,but the effect duration was not more than 84 min,and there was a significant difference between species.The effect of herb stalk and wood fiber was weaker than that of stem bark and bamboo wood fiber.The concentration of niacin in bamboo fiber bundles of Bambusa emeiensis and Bambusa textilis showed significant changes,ranging from 0.02 to 2.58 μg/mL.The highest increase for niacin concentration was observed in Boehmeria nivea stem bark fiber bundles,reaching 3.17 μg/mL,which was more than five times the original concentration and lasted for 72 minutes.The vitamin B6 concentration in the mass transfer fluid of Bambusa textilis and Phyllostachys heterocycla fiber bundle decreased to zero,and the concentration of vitamins B6 in the mass transfer fluid through Boehmeria nivea stem bark fiber bundle increased to two times as much as the original concentration,while the concentration of three vitamins in other fiber bundles increased or decreased slightly.Although plant fiber bundle can lead to an increase or decrease of the three vitamins concentration of the mass transfer fluid,the duration of the effect is only within 84 minutes after the fiber bundle were infiltrated and fulled adequately by the medium fluid.
Key words Plant fiber;MS culture solution;Nicotinic acid;Vitamin B6;Infiltration mass transfer effect;HPLC
基金项目
国家自然科学基金地区基金项目(31660077)。
作者简介 周春长(1994—),男,湖南永州人,硕士研究生,研究方向:林产资源工程。*通信作者,副教授,硕士生导师,从事林产资源工程研究。
收稿日期 2023-09-06
在植物细胞培养生产有用植物次生代谢产物的过程中,营养物质供给方式大体分为2类:一类是直接将植物细胞浸没或间歇性浸没在培养液中进行培养,细胞直接悬浮在营养液中吸取营养物质;另一类是将植物细胞植于凝胶状固态培养基上进行培养。但均因成本、代谢稳定性控制、无菌控制、连续培养、工业化放大等方面存在的问题而未能被商业化应用[1-4]。在探索南方红豆杉愈伤组织大规模连续培养生产紫杉醇时,研究发明了帘状锚固培养生物反应器及培养法[5],即将植物愈伤组织用凝胶粘固接种到垂直悬挂的反应器培养床纤维网上,利用纤维丝的水平毛细浸润作用将培养液从培养床的内壁浸润传质给外壁的愈伤组织,技术的关键在于纤维丝与愈伤组织细胞、培养液间具有高度亲和性,才有利培养液水平浸润传质、植物细胞与纤维丝相结合吸收获取营养物质。因此,纤维丝网能否将MS培养液中的各种溶质以水平浸润方式从纤维网内侧水带传质到外侧,是被选择纤维必须具备的关键功能因素。
烟酸(维生素B3)、维生素B6和维生素B1都是植物细胞代谢过程中自身合成的维生素B族化合物[6-8],属短距离运输类营养物质,参与细胞内诸多重要代谢环节。烟酸和维生素B1作为酶促反应的辅助因子参与包括糖酵解、戊糖磷酸途径和三羧酸循环在内的通用代谢途径中[6,8]。维生素B6除了作为重要的辅酶因子参与生物体基本代谢[9]、生长发育以及对非生物胁迫的响应[10]、植物抗病反应以外[11],还具有抗氧化活性,在细胞内抗氧化防御系统中具有重要的调节作用。研究发现,维生素B6是纯态氧及超氧阴离子有效的清除剂,在强光下,拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)flu突变体会产生纯态氧,导致细胞坏死,而维生素B6处理可以消除这种坏死反应[9]。因此补给外源维生素 B 族物质对植物愈伤组织培养极为重要。
植物纤维主要有种子纤维、茎皮纤维、木纤维和维管束纤维。国内外学者多数围绕不同植物纤维的微观几何特征及功能特性展开研究[12-15]。纤维与流体间相互作用方面,主要围绕纤维通过毛细管效应进行吸水排湿开展研究,如开发功能性纺织纤维材料[16-19]、先进材料表面功能化[19-20]、仿生树木毛细管水分传输开发设计树状包心纱、设计构建可控微液流两性(亲水性与疏水性)分子纤维织物等[17,21-27]。传质(Mass Transfer)是化学工程学的概念,属化学过程工程学的研究领域,是物质浓度在体系中不均匀而发生的质量转移过程[28]。某一组分在两相(或某一相)中的浓度尚未达到相平衡时,这一组分就会由比平衡浓度高的一相转入浓度低的一相,直至两相间浓度达到平衡为止,围绕相关的固-液、气-液、液-液等系统之间的传质过程研究报道较多。曹炳阳等[29]采用分子动力学方法,模拟氩纳米液滴在铂金属模型固体表面的浸润,探讨了纳米结构对流体浸润性质的影响规律。有人利用中空纤维膜生物反应器进行植物细胞培养[30],将植物细胞隔离浸没在中空纤维膜外的营养液中,属于液固直供传质系统。目前利用液体在纤维集束的毛细空间中水平浸润移动转移进行物质质量传递的研究鲜见报道。笔者选择了14种资源丰富、生产容易、较有代表性植物的茎皮、木材、竹材和秸秆4类纤维,采用自主创制的模拟培养床质量传递流程的“纤维水平浸润传质模拟装置”,结合HPLC检测,对16种纤维集束水平浸润传质MS培养液中维生素B族的效应进行了考察,以期为利用纤维集束进行毛细质量传递及相关技术的开发提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
1.1.1 试材。
茎皮纤维:小构树(Broussonetia kazinoki S.et Z.)、苎麻[Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich.];竹材纤维:慈竹(Bambusa emeiensis ‘viridiflavus’)、青皮竹(Bambusa textilis McClure)、毛竹[Phyllostachys heterocycla (Carr.) Mitford cv.Pubescens];木材纤维:白杨(Populus alba)、马尾松(Pinus massoniana Lamb.)、小构树、苎麻;秸秆纤维:荻[Triarrhena sacchariflora (Maxim.) Nakai]、芦竹(Arundo donax)、五节芒[Miscanthus floridulus (Labill.) Warb.ex Schum.et L Laut.]、甘蔗(Saccharum officinarum)、小麦(Triticum aestivum L.)、水稻(Oryza sativa)、玉米(Zea mays Linn),均为自制。